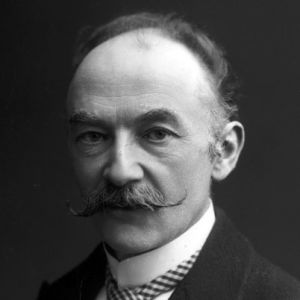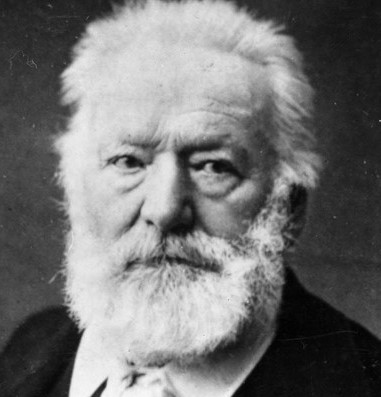Many more eminent scientists, thinkers, writers, politicians and artists of various kinds than is generally realized take or took the possibility of psychical phenomena seriously. Here is a list of more than two hundred of them.
Contents
Introduction
At a time when mainstream science doubts the reality of psi, it can be surprising to learn that some high-profile scientists nevertheless consider it to be real – or at least deserving of scientific study. In fact, many scientists have thought this, as have thinkers and artists of all kinds – especially in the decades since the 1880s, when research societies were first established to investigate psi phenomena.1Cardeña (2014); Gauld (1968). If we believe psi to be real, perhaps persuaded by the scientific literature or by our own experiences, this list of more than two hundred intellectuals reminds us that we are in good company.
Objections can be made to some of the inclusions. Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, the creator of Sherlock Holmes, was as dogmatic in defending séance phenomena as sceptics often are in criticizing it.2Truzzi (1987). The descriptions of personal psi experienced by the Swedish playwright August Strindberg would be of more interest to a clinical psychologist than to a parapsychological researcher. Some held obnoxious views: the pioneering French biologist Alexis Carrel favoured Nazi eugenics, for instance. But taken as a whole, the list overwhelmingly shows that women and men of genius in many areas of life – science, the arts, politics, invention – have shown a lively and at times professional interest in psi, and were irritated by those who tried to stifle it.
It has long been fashionable to argue that psi is simply ruled out by scientific norms – the constraints imposed by physics for instance, or by a knowledge of how the nervous system works. But the belief in the possibility of psi that was held by Nobel prizewinners such as physicists Einstein and Planck, and brain scientists Eccles and Ramón y Cajal, suggests we should treat such claims with caution. Nor should we be distracted by claims that only a psychologist is qualified to detect the myriad ways – whether sensory or cognitive – in which information can be conveyed, considering the presence here of foundational figures in psychophysics,3Fechner (1904). experimental psychology,4Eysenck & Sargent (1993). behaviorism,5Bekhterev (1962). and dynamic psychology, and the fact that some scientists in these fields continue to support the study of psi.6E.g., Cardeña (2014).
In terms of qualifications for inclusion, the people in this list achieved a high degree of eminence in a field independent of parapsychology (although some achieved eminence in the latter also); lived during the past century and a half, the period when psi became a subject of scientific research; and, with the exception of two living Nobel prizewinners, are all deceased.
Excluded are eminent individuals who displayed no knowledge or interest in psi phenomena while pursuing spiritual or occult concerns. Writers and artists are listed if they endorsed psi phenomena, but not if they merely referred to it in their works or if events in their lives could be interpreted as psi, as in the case of the Spanish poet Federico García Lorca who seemed to precisely anticipate the date of his execution five years beforehand in one of his plays.7Cardeña, Iribas, & Reijman (2012). Since nothing is known about his views about psi, he is excluded. Doubts must also remain about the great stage magician and debunker Harry Houdini, who left a code as a means to ascertain whether he could contact his wife after his death,8Ebon (1971). but was vocally hostile to the idea of mediums talking with the dead.
In general, the men and women listed here believed in psi phenomena for the same reasons as do most other people: personal experience (their own or of loved ones) or from reading the research literature. In the first category falls Mark Twain, who dreamed in detail about the future death of his brother,9Ebon (1971). and the visions experienced by Ted Hughes’s mother.10Hughes (1995). In the second category fall Cesare Lombroso and founding members of the Society for Psychical Research (SPR) such as Eleanor Sidgwick and Richard Hodgson, who took a lot of convincing by other researchers before they would endorse the validity of a phenomenon.11Gauld (1968).
The people named here manifested their interest in psi in different, but not necessarily exclusive, ways. One of these can be termed a shift in central interest, in which the individual leaves behind a mainstream scientific activity in order to focus primarily on psi research. The French scientist Charles Richet is a good example of this; in later life he largely abandoned the studies of physiology that had earned him a Nobel prize in order to concentrate on parapsychology and hypnosis, eventually becoming president of both the SPR and the Institut Métapsychique International.
By contrast, a parallel central interest is exemplified by those who maintained their activity in a mainstream scientific endeavor while also pursuing psi research. Good examples are the Sidgwicks. Henry Sidgwick, one of the great modern ethical philosophers,12Freeman (2012). was the first president of the SPR but went on contributing prolifically on subjects relating to ethics, politics and science while holding a professorship at the University of Cambridge. His wife Eleanor (née Balfour), a later SPR president, was a mathematician and educator who served as Principal of Newnham College, only the second college at Cambridge to accept women, while also applying her keen mind to psychical research.
For some of the figures in the list, psi interests were secondary to their other activities. These include Nobel prizewinners Marie and Pierre Curie, who attended séances with Eusapia Palladino and wrote about the importance of studying psi phenomena.13Evrard (2011). Others are Santiago Ramón y Cajal14Sala et al. (2008). and John C Eccles.15Eccles (1982).
Some figures aimed to integrate psi with larger concerns. This applies to William James, a central figure in both psychology and philosophy, who not only participated in psi research and wrote important papers – most famously regarding the medium Leonora Piper, whom he considered his ‘white crow’ – but sought to integrate psi within a larger framework. In physics, David Bohm16Bohm (1986). discussed how psi phenomena might be accommodated within his theory of wholeness and implicate order, while Evans Harris Walker developed a quantum mechanics theory of psi.17Walker (1979). The philosopher Henri Bergson considered psi within his larger discussion of time, consciousness, and evolution.18Barnard (2012).
Psi phenomena have also served as inspiration for both technological and artistic achievements. Among scientists there is the extraordinary case of Hans Berger, inspired by an experience in which his sister, seventy miles away, intuitively felt his brush with death during a military exercise and immediately had their father send him a telegram. When Berger later invented the electroencephalogram (EEG), it was partly to discover if the machine might detect psi.19Berger (1940).
Psi phenomena have been used as a topic for fiction – in the novels of Philip K Dick, the plays of JB Priestley, or the films of Andrei Tarkovsky, among many others. But they have also served as the real-life inspirations for the works themselves. André Breton described a number of ostensible psi phenomena in Nadja, L’Amour Fou and other books, as part of a surrealist exploration of alterations of consciousness and psi phenomena.20Duplessis (2002). The poet James Merrill partly channeled through a Ouija board his Pulitzer and National Book Awards winner The Changing Light at Sandover, proving that not only metaphysical pap comes from automatic writing.21See also Hastings (1991). But can psi eliminate the need for a physical expression of the artwork altogether? This is what František Kupka and Wassily Kandinsky thought earlier in the twentieth century, as does now the performance artist Marina Abramović.22Cardeña, Iribas, & Reijman (2012).
Another category is of authors who worked as psi researcher-participants. This applies to the American novelist Upton Sinclair, whose book Mental Radio23Sinclair (2001). describes a long series of telepathy experiments he carried out himself, with his wife Mary Craig Kimborough acting as the perceiving subject. Another influential book was JW Dunne’s An Experiment with Time,24Dunne (1934/1981). in which the author discussed in detail a number of his ostensibly precognitive dreams.
Some had a veiled interest in psi. One is the painter Hilma af Klint, who in addition to her main activity of painting portraits and plants conducted a decades-long program of other painterly activities, based on either direct automatic writing and painting, or on an elaboration of messages that she believed she received from higher spiritual sources.
In the realm of politics at least two prime ministers, Britain’s Arthur Balfour and Canada’s William Lyon Mackenzie King, privately consulted with mediums without this impacting on their professional work.25Ebon (1971).
In the category of explicit acceptance can be cited a casual mention by the Russian dissident writer Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn in his book The Gulag Archipelago of psi abilities possessed by one of his former cellmates: ‘There is no doubt that he had the gift of precognition’, Solzhenitsyn wrote. ‘More than once he went around in the cell in the morning and pointed: Today they are going to come for you and you. I saw it in my dream. And they came and got them.’26Solzhenitsyn (1973). The pioneering computer scientist Alan Turing27Turing (1950). referred to the ‘overwhelming’ statistical evidence for telepathy in a landmark paper on artificial intelligence. A different sort of example is Otto Stern, who was so fearful of the damaging psychokinetic effects that fellow physicist Wolfgang Pauli seemed to leave in his wake that he barred Pauli from entering his laboratory.
Finally there are those who can be characterized as true sceptics, being open to the possibility of psi phenomena without having arrived at a definite conclusion.28Cardeña (2011). In this category we find Albert Einstein, who in a sympathetic preface to Sinclair’s Mental Radio confessed that his original disbelief had softened as he became more familiar with psi. Similarly, Max Planck expressed support of research by fellow physicist Oliver Lodge’s investigations of psi phenomena, considering them plausible.
Note: this list may underrepresent people who fulfill the criteria, and tends to favour authors from the American and European continents, for whom information was more easily accessible. Most entries contain a single reference, although some made many contributions. Some of this information appeared previously in an issue of Mindfield, the bulletin of the Parapsychological Association.
Etzel Cardeña
Nobel Prizewinners
Henri Bergson (1859–1941), philosopher, 1927 Nobel Prize in Literature, president of the Society for Psychical Research and theoretician of consciousness and psi.29Barnard (2012). (See article)
Bjørnstjerne Bjørnson (1832–1910), 1903 Nobel Prize in Literature, wrote an article about a person said to be psychic.30Bjørnson (1909).
Pearl S Buck (1892–1973), 1938 Nobel Prize in Literature, visited JB Rhine’s parapsychology meetings.31Horn, S. (2009).
Nicholas Murray Butler (1862–1947), 1931 Nobel Prize in Peace, President of Columbia University, philosopher and diplomat, wrote about psi32Butler (1886). and helped organize the American Society for Psychical Research.
Alexis Carrel (1873–1944), 1912 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, discussed anomalous healing in a book.33Carrel (1939).
James Earl (Jimmy) Carter, Jr. (1924-2024), 39th President of the USA and, following his presidency, founder of many humanitarian projects, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Peace Prize. He revealed in an interview and in his autobiography the use of a Stargate psychic to successfully locate a missing aeroplane, an event that he called ‘inexplicable’.34Carter (2016).
Winston Churchill (1874-1965), 1953 Nobel Prize in literature, prime minister of the United Kingdom during World War II and afterwards. There are accounts that his momentary intuitions might have saved his and others’ lives, described for instance in his widow’s memoirs.35Excerpta (1963).
Arthur Holly Compton (1892–1962), 1927 Nobel Prize in Physics, was supportive of psi in his correspondence with JB Rhine.36Horn (2009).
Marie Curie (1867–1934), 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics, 1911 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, participated in séances with Eusapia Palladino and wrote of the importance of research in parapsychology.37Evrard (2011).
Pierre Curie (1859–1906), 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics, participated in séances with Eusapia Palladino and wrote of the importance of research in parapsychology.38Evrard (2011). (See article)
John Eccles (1903–1997), 1963 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, edited a book discussing psi and participated in related conferences.39Eccles (1982).
Albert Einstein (1879–1955), 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics, wrote the preface to a telepathy book40Sinclair (2001). and commented, ‘We have no right to rule out a priori the possibility of telepathy. For that the foundations of our science are too uncertain and incomplete.’41Ehrenwald (1978).
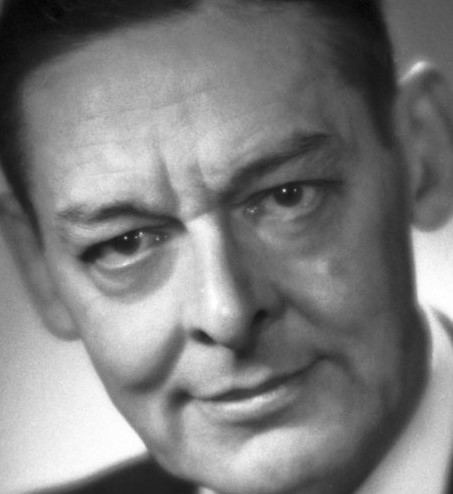
T. S. Eliot (1888–1965), 1948 Nobel Prize in Literature, a major figure in poetry and essay, ‘regarded highly’ the theory of precognition by Dunne and reprinted his An Experiment with Time while he was director of Faber and Faber. He described a similar view of time in his poem Burnt Norton.42Stevenson (2018), 125.
Brian Josephson (b 1940), 1973 Nobel Prize in Physics, has written about psi and been a staunch advocate of psi research for decades.43Josephson (n.d.).
Maurice Maeterlinck (1862–1949), 1911 Nobel Prize in Literature, wrote on ostensible psi phenomena.44Maeterlinck (1969).
Thomas Mann (1875–1955), 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature, attended and reported on séances.45Mann (2005).
Guglielmo Marconi (1874–1937), 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics, developer of radio and radio telegraphy, interested in spiritualism; he wanted to invent a technology to communicate with the deceased.46Goff (2005).
Toni Morrison (1931–2019), 1993 Nobel Prize in Literature, among various awards, mentioned in an interview coming to believe in aspects that had been dismissed in her education, and gave an example of her mother and others seeing the apparition of an aunt who, at that time and unbenownst to them, had died.47Nicholson (1988).
Kary Banks Mullis (b 1944), 1993 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, has participated in psi research and spoken in support of it.48Radin (2006).
Wolfgang Pauli (1900–1958), 1945 Nobel Prize in Physics, discussed with Carl Jung the notion of synchronicity and was believed, by himself and by colleagues, to have an interfering psychokinetic effect on machines.49Gieser (2005). (See Otto Stern, below.)
Jean Perrin (1870–1942), 1926 Nobel Prize in Physics, was a member of the Institut Général Psychologique’s (IGP) Group of Study of Psychic Phenomena.50Courtier (1908).
Max Planck (1858–1947), 1918 Nobel Prize in Physics and author of quantum theory, expressed his interest in psychical research in his correspondence.51Sommer (2014).
Sully Prudhomme (1839–1907), 1901 Nobel Prize in Literature, participated in the Société de Psychologie Physiologique’s committee for the study of telepathy.52Collectif (1891).
Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852–1934), 1906 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, researched hypnosis and psi phenomena and wrote a book about them (destroyed during the Spanish Civil War).53Sala et al. (2008).
Sir William Ramsay (1852–1916), 1904 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, discoverer of the noble gases, collaborator with Lord Rayleigh, was a member of the SPR and corresponded with Rayleigh on the SPR’s research activities.54Oppenheim (1986).
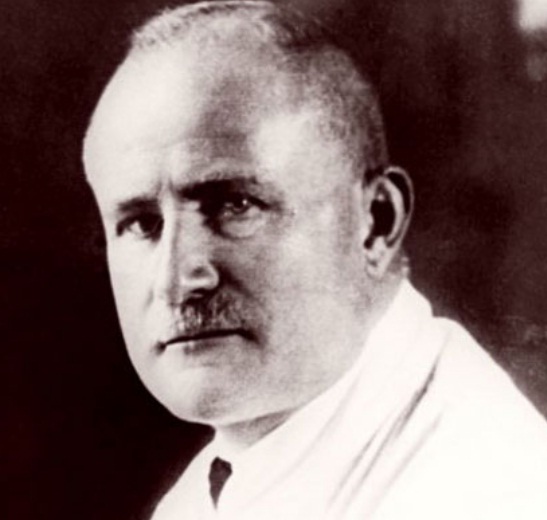
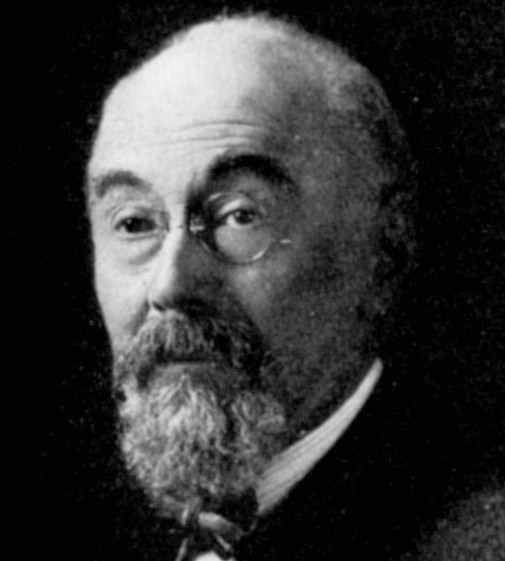
Charles Richet (1850–1935), 1913 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, founded the Annales des Sciences Psychiques, president of the Society for Psychical Research (1905), and of the Institut Métapsychique International (1923). (See article)
George Bernard Shaw (1856–1950), 1925 Nobel Prize in Literature, best known for his very influential plays, including Pygmalion and Arms and the Man. He attended meetings of the Society for Psychical Research with psi researcher Frank Podmore and mentioned incidents of ostensible psi.55Reichbart (2019).
Albert Schweitzer (1875–1965), 1925 Nobel Prize in Peace, reported the paranormal phenomena he observed in Africa and remarked that he would like to carry out psi research.56Schweitzer (1931).
Glenn Seaborg (1912–1999), 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the investigation of traunsuranium elements, co-wrote with Margaret Mead a praising statement about a book on parapsychology.57Bowles & Hynds (1979).
Isaac Bashevis Singer (1903-1991), 1978 Nobel Prize in Literature and towering figure of the Yiddish literary movement. He mentioned in an interview that ‘it is my conviction that telepathy and clairvoyance and premonitions and all these things are really a part of nature’.58Kleinman (1970).
Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn (1908–2008), 1970 Nobel prizewinner in literature, mentions precognition as a fact in his work.59Solzhenitsyn (1973).
Otto Stern (1888–1969), 1943 Nobel Prize in Physics, is said to have banned fellow physicist Wolfgang Pauli from his lab, for fear that Pauli’s involuntary psychokinetic effect would interfere with the machinery there.60https://www.ethistory.ethz.ch/besichtigungen/objekte/paulieffekt/
John William Strutt, Lord Rayleigh (1842–1919), 1904 Nobel Prize in Physics, discovered of argon, collaborator of William Ramsay, president of the Society for Psychical Research.61Gauld (1968).
Eugene Wigner (1902–1995), 1963 Nobel Prize in Physics, encouraged research on physics and psi.62Kaiser (2011).
JJ Thompson (1856–1940), 1906 Nobel Prize in Physics, member of the governing council of the Society for Psychical Research for 34 years.63Downard (2021).
WB Yeats (1865–1939), 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature, member of the Society for Psychical Research, wrote extensively about psi and esoterism.64Yeats (1925/2013).
Other Eminent Figures: Physics, Chemistry, Engineering, Invention
Jacques-Arsène d’Arsonval (1851–1940), physician, physicist, and inventor, led the IGP and carried out research with a spirit medium.65Marmin (2001).
John Logie Baird (1888–1946), engineer and inventor of television, attended spiritist séances and was persuaded by them.66Goff (2005).
Sir William Barrett (1845–1925): Chair of physics at the Royal College of Science in Dublin, Fellow of the Royal Society, and founder and president of the Society for Psychical Research.67Gauld (1968). (See article)
Olivier Costa de Beauregard (1911–2007), quantum physicist, published on parapsychology, first under the pseudonym E. Xodarap, and considered psi phenomena as to ‘be expected as very rational’.68Beauregard (1975).
Alexander Graham Bell (1847–1922), inventor of the telephone, thought that the device might allow communication with the dead.69Goff (2005).
John Stewart Bell (1928–1990), physicist, developer of the Bell theorem, employee of the European Council for Nuclear Research (CERN), originator of the Bell theorem, wrote about keeping an open mind regarding psi.70Kaiser (2011).
David Bohm (1917–1992), quantum theoretician, sought to integrate his theory with psi.71Bohm (1986).
Édouard Branly (1844–1940), physicist, inventor of a component of wireless telegraphy, member of the French Academy of Sciences, was a member of the IGP’s Group of Study of Psychic Phenomena.72Courtier (1908).
Alexander Butlerov (1828–1886), chemist, pioneer of the theory of chemical structure and discoverer of various elements, researched ostensible psychic manifestations and wrote articles about them.73Rawson (1978).
Chester Carlson (1906–1968), physicist and inventor of electrophotography, donated money to and was interested in psi research.74Stevenson (2006).
Sir Arthur C Clarke (1917–2008), science and science fiction writer and inventor, discussed psi in his novels and non-fiction, becoming increasingly, but not completely, sceptical about the paranormal.75Clarke (2001).
Gérard Cordonnier (1907–1977), mathematician, engineer, winner of the Arts, Sciences and Letter Silver Medal, wrote on psi.76Lorenzato (1978).
Sir William Crookes (1832–1919), chemist, physicist, and inventor, conducted research on DD Home and spiritualism, president of the Society for Psychical Research.77Oppenheim (1988). (See article)
JW Dunne (1910–1949), aeronautical engineer, wrote An Experiment with Time, a book about precognition.78Dunne (1981).
Freeman Dyson (1923–2020), theoretical physicist and mathematician who made fundamental contributions to various areas of science, wrote a foreword to a book on psi phenomena in which he stated: ‘ESP is real, as the anecdotal evidence suggests, but cannot be tested with the clumsy tools of science.’79Dyson (2007), x.
Thomas Alva Edison (1847–1931), inventor of electric light and sound recording, among other things, was convinced by some psi demonstrations and proposed that instruments could be developed to communicate with the deceased.80Goff (2005).
Harold Eugene Edgerton (1903–1990), professor of electrical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, participated in research on remote viewing.81Schwartz (2001).
Gerald Feinberg (1933–1992), physicist, worked at Columbia and Princeton Universities, considered precognition to be at the base of most, or perhaps all, psi phenomena.82Feinberg (1975).
Camille Flammarion (1842–1925), astronomer and writer, founder and first president of the Société Astronomique de France, wrote on psi and mediumship.83Flammarion (1907). (See article)
J.T. Fraser (1923–2010), engineer and inventor, founded the multidisciplinary study of time. In his most important book, he refers positively to the naturalistic and experimental work on precognition by the Rhines.84Fraser (1966).
Richard Buckminster Fuller (1895–1983), systems theorist, inventor, talked about the reality of telepathy.85Fuller (n.d.)
George Gamow (1904–1968), physicist, wrote on the ostensible macro-PK effect called the Pauli Effect.86Gamow (1966).
Arnaud de Gramont (1861–1923), physicist, member of the French Académie des Sciences, founding member of the Institut Métapsychique International.87Institut Métapsychique International (n.d.).
John Hays Hammond, Jr. (1988–1965), inventor and foundational figure of electronic remote control. He conducted successful telepathy experiments with the psychic Eileen Garrett whom he placed in a Faraday cage, concluding that her ability could not be explained in terms of electromagnetic frequencies.88Brooks (2012).
Heinrich Hertz (1857–1894), physicist, showed the existence of electromagnetic waves, was a member of the Society for Psychical Research.89Sommer (2014).
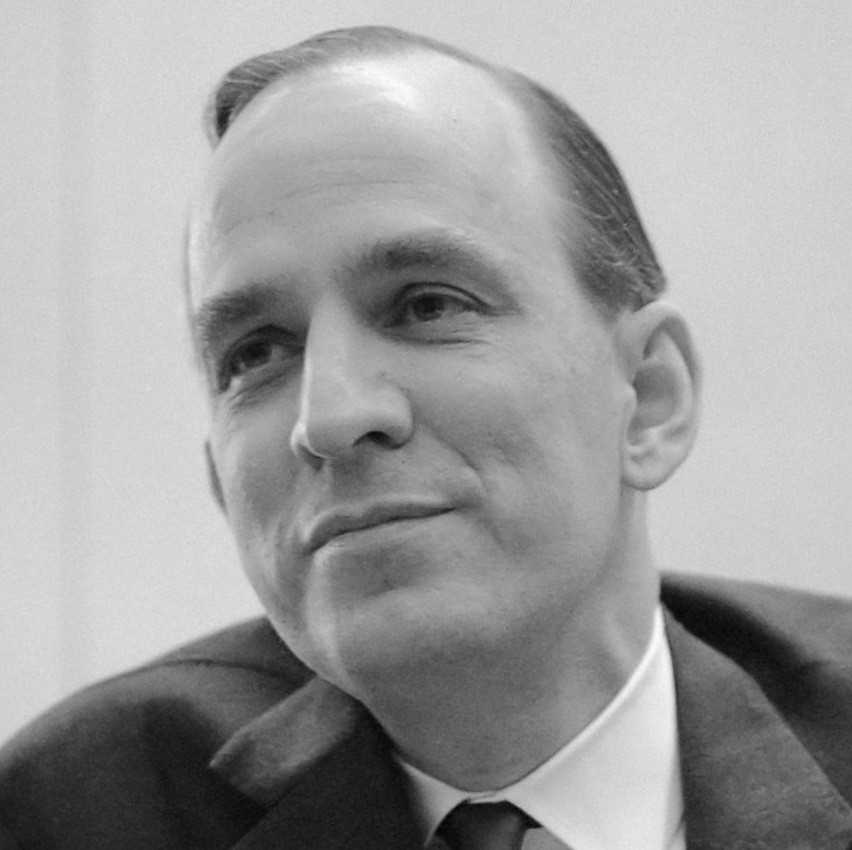
Robert Jahn (1930–2017), dean of engineering at Princeton University, pioneer of deep space propulsion, founded the Princeton Engineering Anomalies Research laboratory to study mind-machine interactions and other psi phenomena.90Schultz (2017). (See article)
Ernst Jordan (1902–1980), quantum physicist, wrote on quantum mechanisms and psi.91Jordan (1951).
Sir Oliver Lodge (1851–1940), physicist and mathematician, developer of wireless telegraphy, principal of Birmingham University, president of the Society for Psychical Research, wrote on mediumship and survival.92Lodge (1916). (See article)
Henry Margenau (1901–1997), Higgins Professor of Physics at Yale and staff at Princeton and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, philosopher of science, wrote favourably about parapsychology.93Margenau (1970).
James Smith ‘Mac’ McDonnell (1899–1980), engineer and chair of the McDonnell-Douglas corporation, supported research in parapsychology.94Thalbourne (1995).
Edgar Dean Mitchell (1930–2016), aeronautical engineer, sixth person to walk on the moon, founded the Institute of Noetic Sciences, by which research on psi is conducted, and published a psi study himself.95Mitchell (1971).
Edward Pickering (1846–1919) astronomer and physicist, director of the Harvard College Observatory, wrote on psi.96Bowditch et al. (1886).
Sir Alfred Pippard (1920–2008), Cavendish Professor of Physics, Cambridge, gave an address to a joint SPR/Parapsychological Association on his mother’s telepathic experiences.97Pippard (1982).
Michael Polanyi (1891–1976) made important contributions to various fields including chemistry, economics, and epistemology, including the concepts of personal and tacit knowledge. He was cognizant of JB Rhine’s work and remained open to it, mentioning the parapsychological explanation as the simplest one.98Polanyi (1958).
Archie E Roy (1924–2012), professor of Astronomy, University of Glasgow, SPR president, wrote on psychical research.99Roy (1990).
Giovanni Schiaparelli (1835–1910), astronomer, historian of science and senator, researched Eusapia Palladino.100Gauld (1968).
Richard Shoup (1943–2015), computer scientist, innovator in digital animation and winner of an Emmy Award and an Academy Award, proposed a time symmetric theory of psi.101Radin (2015).
Balfour Stewart (1828–1887), physicist, member of the Royal Society, president of the Society for Psychical Research.102See here.
FJM Stratton (1881–1961), Professor of Astrophysics and Director of the Solar Physics Observatory at Cambridge, president of the Society for Psychical Research.103See here.
Julien Thoulet (1843–1936). Professor of Mineralogy at the University of Nancy, oceanographer,104Mills (2009). described a psi event in a letter to Charles Richet.105Kripal (2010).
Cromwell Fleetwood Varley (1828–1883), engineer and developer of telegraph technology, conducted physics experiments with mediums.106Noakes (2019).
Wernher von Braun (1912-1977), German aerospace engineer, an SS member during World War II and a central figure in Nazi rocket production, who later emigrated to the US and helped develop the NASA Apollo spacecrafts. Von Braun participated in a meeting to explore supporting psi research and was tested with an ESP testing machine.107Targ (2012).
Evan Harris Walker (1935–2006), physicist and inventor, developed a quantum explanation of psi.108Walker (1979).
Arthur M Young (1905–1995), polymath, helicopter inventor, sought to integrate parapsychology with other branches of science.109Young (1976).
Johann Karl Friedrich Zöllner (1834–1882), astrophycist who provided a measure of the sun’s radiance and created optical illusions. He was a psychical researcher and wrote on his experiments with medium Henry Slade, who very likely was fraudulent.110Carrington (1907).
Mathematicians
Burton H Camp (1880–1980), president of the Institute of Mathematical Sciences, wrote that the statistical analyses conducted by Rhine and his team were ‘essentially valid’.111Camp (1937).
Augustus de Morgan (1806–1871), mathematician and logician, advanced the study of induction. His wife Sophia, under a pseudonym, wrote a book reporting their investigations on psychic phenomena, with a pseudonymous preface by De Morgan, in which these phenomena were not considered per se precluded by science and a truly agnostic view about psychic phenomena was proposed.112De Morgan (1863).
Sir Ronald A Fisher (1890–1962), statistician and geneticist, corresponded with JB Rhine and published articles on statistical analyses in parapsychology.113Fisher (1930).
Thomas Greville (1910–1988), statistician, professor at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, editor of the Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, developed statistical techniques for psi experiments.114Greville (1938).
Irving Good (1916–2009), statistician and cryptologist, colleague of Alan Turing, suggested a physiological method to study nonconscious psi.115Good (1961).
Hans Hahn (1879–1934), mathematician and philosopher, was vice-president of the Austrian Society for Psychical Research and collaborated in research on psi.116Sommer (2013).
John Littlewood (1885–1977), Ball Professor of Mathematics, Cambridge, fellow of the Royal Society, conducted card guessing experiments and wrote on their statistics.117Littlewood (1968).
Eleanor Sidgwick (1845–1936), mathematician, principal of Newnham College, president of the Society for Psychical Research.118Gauld (1968). (See article)
Alan Turing (1912–1954), mathematician, pioneer of computer science and artificial intelligence, wrote of the ‘overwhelming’ statistical evidence for telepathy.119Turing (1950).
Psychologists, Social Scientists, Neuroscientists, Biologists and Physicians
Roberto Assagioli (1888–1974), psychiatrist, pioneer of humanistic and transpersonal psychology, wrote a book on psi.120Assagioli (1958).
David Bakan (1921–2004), professor of psychology at the Universities of Chicago and York, discussed biblical prophecy and contemporary psi research in his courses.121Bakan, Merkur, & Weiss (2009).
Margaret Bancroft (1854–1912), who pioneered a holistic treatment for developmentally-disabled children and founded a specialized school still open today, sat in and investigated the mediumship of Leonora Piper.122Gauld (2022).
Vladimir Bekhterev (1856–1927), neurologist and reflex psychologist, studied psi in humans and animals.123Bekhterev (1962).
Hans Berger (1873–1941), neurologist, invented the electroencephalogram, inspired by a telepathic event with his sister.124Berger (1940).
Filippo Bottazzi (1867–1941), physiologist, biochemist, wrote a book on mediumistic phenomena.125Bottazzi (2011).
Henry Pickering Bowditch (1840–1911), physician, dean of the Harvard Medical School, founding member of the Society for Psychical Research, wrote on psi.126Bowditch et al. (1886).
William Brown (1881–1952), director of the Institute of Experimental Psychology at Oxford University, supported psi research.127Shepard (1978).
Luther Burbank (1849–1926), botanist, creator or developer of many species, founder of agricultural science, described his own and his family’s telepathic abilities in his autobiography.128Prince (1928).
Dorothy Tiffany Burlingham (1891–1979), pioneer of child psychoanalysis and co-founder of the Hampstead Clinic in London (currently the Anna Freud Centre). Wrote a paper positing psi processes among mothers and children.129Burlingham (1953).
Rémy Chauvin (1913–2009), biologist, honourary professor at La Sorbonne, researched and wrote on animal psi.130Chauvin (1985).
Irvin L Child (1915–2000), chair of psychology at Yale University, wrote a supportive metaanalysis of the Maimonides dream research program.131Child (1985).
Hans Driesch (1867–1941), biologist and philosopher, wrote a book on psi, and was president of the Society for Psychical Research.132Driesch (1933). See also here.
Frederik Willem van Eeden (1860–1932), psychiatrist, writer, and progressive thinker, participated in séances and wrote about lucid dreaming.133Gauld (1968).
HJ Eysenck (1916–1997), psychologist, researcher in personality, intelligence, and psychotherapy, supported the validity of some psi phenomena and criticized scientistic dogmatism.134Eysenck & Sargent (1993).
Gustav Fechner (1801–1887), physicist, one of the founders of experimental psychology, participated in séances and wrote about the possibility of survival after death.135Fechner (1904).
Sándor Ferenczi (1873–1933), central theorist in psychoanalysis, wrote on psi phenomena in development and therapy and communicated with Freud about it.136Ferenczi (1955).
Théodore Flournoy (1854–1920), psychologist, professor at the University of Geneva, wrote important books on dissociation without discarding the possibility of psi processes.137Flournoy (2007). See also Freeman (2012). (See article)
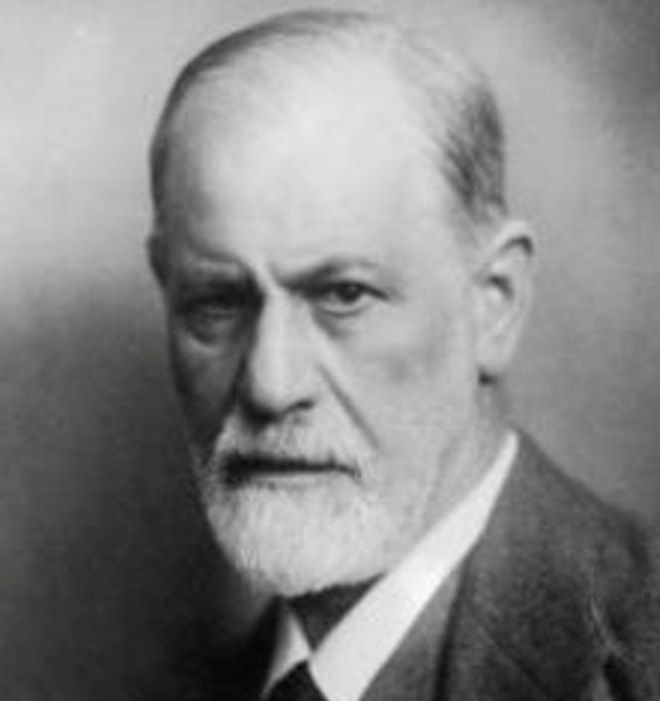
Sigmund Freud (1856–1939), founder of psychoanalysis, wrote a number of papers on psi in psychotherapy.138Devereux (1953).
Sir Ronald A Fisher (1890–1962), statistician and geneticist, corresponded with JB Rhine and published articles on statistical analyses in parapsychology.139Fisher (1924).
William Hewitt Gillespie (1905–2001), President of the International Psychoanalytical Association, Freud Memorial Professor of Psychoanalysis at University College, London, wrote supportively of psi phenomena.140Gillespie (1953).
Karl Gruber (1881–1927), zoologist, professor at Munich Polytechnic, conducted psi research on animals.141Gruber (1925).
Guðmundur Hannesson (1866–1946), physician, founder of the Icelandic Scientific Society and rector of the University of Iceland, investigatedthe medium Indriði Indriðason.142Gissurarson & Haraldsson (1998).
Sir Alister Hardy (1896–1985), Linacre Professor of Zoology at Oxford, founder of the Religious Experience Research Unit at Oxford, president of the Society for Psychical Research, wrote on psi and religion.143Hardy (1971).
Raúl Hernández-Peón (1924–1968), neurophysiologist of sleep, sought to integrate psi and neurophysiology144Hernández-Peón (1968).
James Hillman (1926–2011), psychologist, Jungian author, wrote on psi and depth psychology.145Hillman (1970).
Sir Julian Huxley (1887–1975), evolutionary biologist and first director of UNESCO, mentioned psi supportively in his writing.146Huxley (1965).
Aniela Jaffé (1903–1991), psychologist, Jungian author, wrote on psi and synchronicity.147Jaffé (1967).
William James (1842–1910), psychologist and philosopher, president of both the British and the American Societies for Psychical Research.148James (1960). (See article)
Pierre Janet (1859–1947), pioneer in the study of dissociation, had success in experiments on hypnosis and psi (but later became cautious about psi).149Ellenberger (1970).
Carl G Jung (1875–1961), founder of analytical psychology, wrote on synchronicity and ostensible psi phenomena.150Gieser (2005). (See article)
Elizabeth Kübler-Ross (1926–2004), psychiatrist, proponent of the hospice care movement, wrote on near-death experiences and the possibility of survival.151Kübler-Ross (1991).
AN Leontiev (1903–1979), head of the psychology department at Moscow University, investigated remote viewing.152Zinchenko, Leont’ev, Lomov, & Luria (1974).
Jacques Jean Lhermitte (1877–1959), neurologist and neuropsychiatrist, clinical director at the Salpêtrière hospital, member of the Institut Métapsychique International.153See here.
Cesare Lombroso (1835–1909), criminologist and physician, wrote a book on spiritualism and psi.154Lombroso (1909).
Alexander Luria (1902–1977), neuropsychologist, wrote about parapsychology.155Zinchenko, Leont’ev, Lomov, & Luria (1974).
Elizabeth Lloyd Mayer (1947–2005), psychoanalyst, professor at the University of California, investigated psi in depth after a psychic traced a valued stolen possession.156Mayer (2007).
William McDougall (1871–1938), psychology professor at Harvard and later at Duke, president of both the American and the British Societies for Psychical Research.157Asprem (2010). (See article)
Margaret Mead (1901–1978), cultural anthropologist, helped the Parapsychological Association become a member of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and wrote a supportive introduction to a remote-viewing book.158Mead (1977).
Paul Meehl (1920–2003), psychologist and philosopher of science, wrote on the likely compatibility of science and ESP.159Meehl & Scriven (1956).
Thomas Walter Mitchell (1869–1944), physician, for many years editor of the British Journal of Medical Psychology, president of the Society for Psychical Research.160See here.
John Muir (1838–1914), geologist and naturalist, recounted in a letter having an accurate premonition of encountering an unexpected friend in a valley.161Prince (1928).
Gardner Murphy (1895–1979), president of the American Psychological Association and of the Society for Psychical Research,162See here. wrote extensively on human potentials and on psi.163Murphy (1961). (See article)
Traugott Konstantin Oesterreich (1880–1949), psychologist and philosopher, professor in Tübingen, wrote on spirit possession and psi.164Oesterreich (1921).
Humphry Osmond (1917-2004), pioneer in the study and use of psychedelic drugs, coined the term psychedelic and organized and participated in conferences on parapsychology and psychedelics.165Pleasant (1964).
Sir Alan S Parkes (1900–1990), researcher at University College, London, on reproductive biology, organized and participated in a symposium on psi.166Ciba Foundation (1965).
Candace Pert (1946–2013), neuropharmacologist, chief of the Section on Brain Biochemistry of the Clinical Neuroscience Branch, National Institute of Mental Health, was interested in psychokinetic effects on living systems and subtle energies.167Pert (1996).
Théodule-Armand Ribot (1839–1916), psychologist, professor at the Collège of France and La Sorbonne, published papers on psychical research in his journal Revue Philosophique.168Alvarado & Evrard (2013).
Robert Rosenthal (1933-2024), one of the most important psychologists of the 20th centure, investigated the Pygmalion effect in learning.169Cardeña (2024).
Sante de Sanctis (1862–1935), foundational figure of Italian psychology, psychiatry, and pedagogy, investigated ostensible psi phenomena.170Price (1939).
Hans Schäfer (1906–2000), professor and director of the Department of Physiology at the University of Heidelberg, epidemiologist, wrote about psi.171Schaefer (1952).
Rocco Santoliquido (1854–1930), physician and Director General of Public Health, investigated a medium, and was founder and president of the Institut Métapsychique International.172See here.
Emanuel Schegloff (1937-2024), distinguished professor of sociology at UCLA, co-creator of conversation analysis, wrote about ostensible ESP puns in communication.173Schegloff (2003).
Pitirim Sorokin (1889–1968), founder and director of the Department of Sociology at Harvard, wrote an introduction to a book on psi.174Sorokin (1951).
Mabel St Clair Stobart (1862–1954), founder of the Women’s Sick and Wounded Convoy Corps (1912) and the Women’s National Service League (1914), wrote about spiritualism.175Stobart (1923).
Wilhelm Stekel (1868–1940), prolific writer and one of the first associates of Freud, authored a book about telepathy in dreams.176Stekel (1918).
John R Swanton (1873–1958), president of the American Anthropological Association and editor of American Anthropologist, endorsed parapsychology.177Swanton (1953).
Leonid I Vasiliev (1891–1966), professor of physiology at Leningrad University, extensively researched psi and suggestion at a distance.178Vasiliev (2002).
Alfred Russel Wallace (1826–1923), co-creator of the theory of evolution, investigated and was a supporter of spiritualism.179Gauld (1968).
William Grey Walter (1910–1977), neurophysiologist and robot inventor, wrote on the use of the EEG to investigate psi.180Walter (1970).
Philip Zimbardo (1933–2024), one of the foremost social psychologists in history, educator of psychology, and president of the American Psychological Association. He co-signed a call for an open, informed study of psi phenomena.181Cardeña (2014).
Humanities, Philosophers
Bhikhan L Atreya (1897–1967), professor of philosophy at Banaras Hindu University, expert on Hinduism, carried out research and wrote on parapsychology.182Atreya (1952).
Samuel Bergman (1883–1975), philosopher of physics, dean of the Hebrew University, wrote a book on telepathy.183Shepard (1978).
Émile Boirac (1851–1917), philosopher, president of the Grenoble and Dijon universities, researched Eusapia Palladino, wrote a book on psychical research.184Boirac (1917).
Kenneth E Boulding (1910–1993), economist, systems scientist, philosopher, president of the American Association for the Advancement of Sciences, declared to the Washington Star in 1979: ‘The evidence of parapsychology can’t just be dismissed out of hand’.185Anonymous (1990).
CD Broad (1887–1971), Knightsbridge Professor of Moral Philosophy at Cambridge, president of the Society for Psychical Research.186See here. (See article)
Kenneth Burke (1897–1993), literary theorist, discussed psi phenomena in the context of creativity.187Burke (1970).
Rudolf Carnap (1891–1970), philosopher and member of the Vienna Circle, wrote on the importance of researching psi.188Carnap (1963).
Pierre Teilhard de Chardin (1881–1955), philosopher and palentologist, wrote on the evolution of psi abilities in The Phenomenon of Man.189Teilhard de Chardin (1965).
CTK Chari (1909–1993), head of the department of philosophy at Madras Christian College, wrote on philosophy of physics and psi.190Chari (1975).
Ernesto de Martino (1908–1965), historian of religion and anthropologist, wrote on the link between ethnology and parapsychology.
Jacques Derrida (1930–2004), philosopher, founder of deconstructionism, wrote an essay discussing the nature of telepathy and its relation to psychoanalysis.191Derrida (1981).
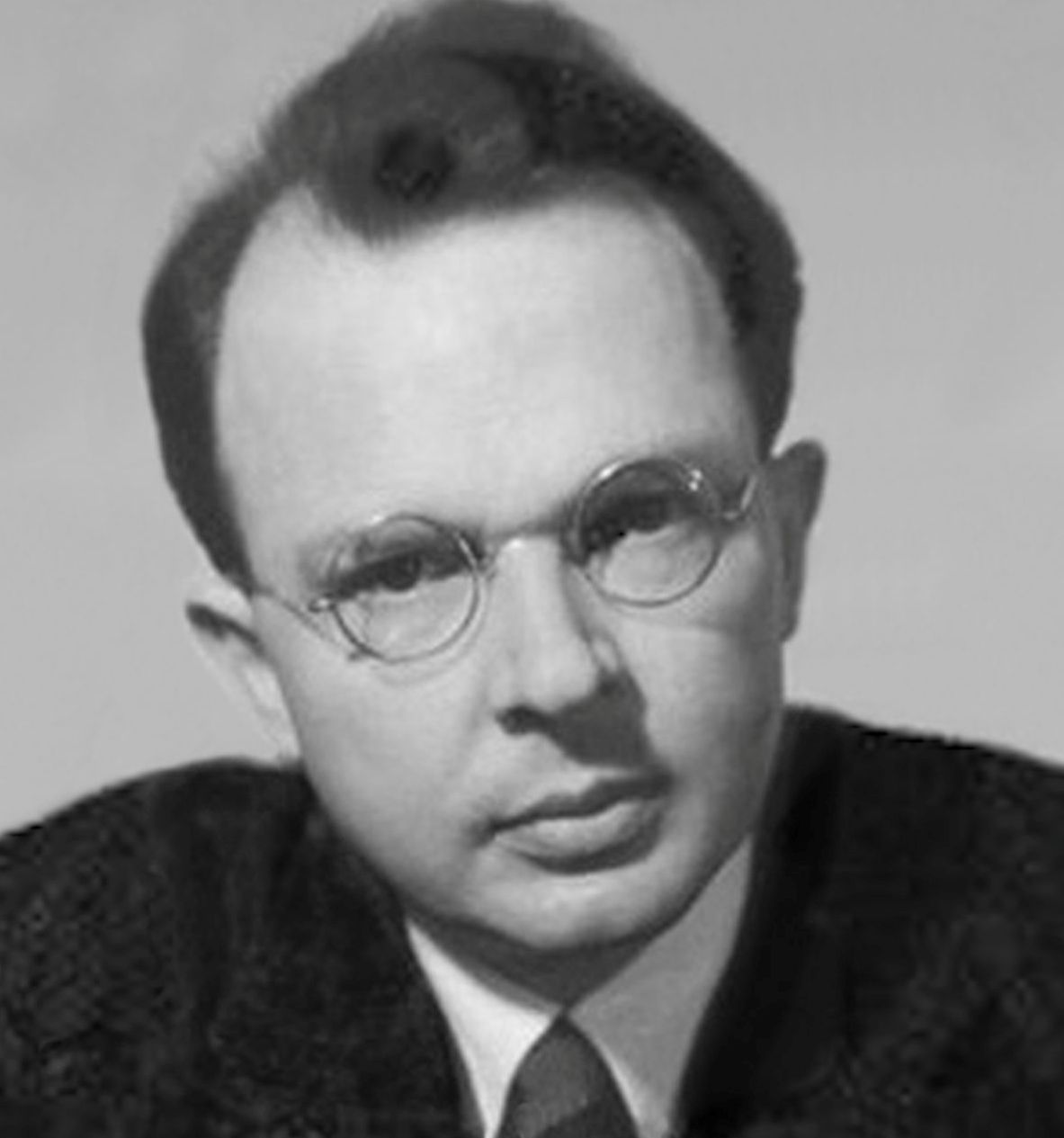
Max Dessoir (1867–1947), philosopher, psychologist, professor at the University of Berlin, coined ‘parapsychology’ and other psi terms.192Dessoir (1889). (See article)
ER Dodds (1893–1979), classical scholar, Regius Professor of Greek (Oxford), president of the Society for Psychical Research.193Dodds (1934), also see here.
CJ Ducasse (1881–1969), professor of philosophy at Washington and Brown Universities, wrote on parapsychology and was a Board member of the American Society for Psychical Research.194Ducasse (1961). (See article)
Mircea Eliade (1907–1986), Professor at the University of Chicago, historian of religion and fiction writer, asserted that real paranormal phenomena were at the base of some religious beliefs.195Eliade (2006).
Antony Flew (1923–2010), philosopher of religion, while not convinced about psi phenomena, opined that there was ‘much interesting and suggestive evidence’.196Flew (1970).
Isaac K Funk (1839–1912), lexicographer, editor, founder of Funk & Wagnalls, wrote on psi phenomena.197Funk (1907).
Maurice Garçon (1889–1967), lawyer, writer, conjurer, member of the Académie Française, researched psi phenomena.198Garçon (1929).
James H Hyslop (1854–1920), philosopher, psychologist, professor at Columbia University, wrote extensive on psi.199Hyslop (1906). (See article)
LP Jacks (1860–1955), professor of philosophy and principal at Manchester College, Oxford, president of the Society for Psychical Research.200See here.
Andrew Lang (1844–1912), writer and anthropologist, president of the Society for Psychical Research.201See here and here.
Gabriel Marcel (1889–1973), philosopher, member of the Académie des Sciences Morales et Politiques, honourary president of Institut Métapsychique International.202Marcel (1956).
Gilbert Murray (1866–1957), classicist, professor at Oxford and Harvard universities, vice president of the League of Nations Society after World War I, president of the Society for Psychical Research.203See here.
Frederic Myers (1843–1901), classical scholar and poet, president and one of the main founders of the Society for Psychical Research.204Gauld (1968). (See article)
Haraldur Níelsson (1868–1928), theologian and spiritualist, first rector of the University of Iceland, investigated the medium Indriði Indriðason.205Swatos & Gissurarson (1997).
HH Price (1899–1984), philosopher, Wykeham Professor of Logic at Oxford, president of the Society for Psychical Research.206Price (1939). Also see here.
Adolf Reinach (1883–1917), pioneer phenomenologist and language and law theoretician, documented and discussed instances of soldiers’ foreboding (precognition) in WWI of their impending death.207Baltzer-Jaray (2016).
Josiah Royce (1855–1916), philosopher, professor at the University of California and Harvard, member of the American Society for Psychical Research, wrote on psi.208Royce (1889).
Ferdinand de Saussure (1857–1913), linguist and semiotician, attended séances of Hélène Smith (Catherine-Elise Müller) and analyzed her created languages.209Flournoy (1911/2007).
FCS Schiller (1864–1937), professor of philosophy at the Universities of Oxford, Cornell, and Southern California, president of the Society for Psychical Research, supported the epistemological foundation of parapsychology.210Schiller (1914).
Henry Sidgwick (1838–1900), Knightsbridge Professor of Moral Philosophy at Cambridge, President of the Society for Psychical Research.211Gauld (1968). (See article)
Kees van Peursen (1920–1996), philosopher and theologian, professor of philosophy at Groningen and Leiden Universities, wrote on psi.212Van Peursen (1959).
AW Verrall (1851–1912), classics scholar and first King Edward VII Chair of English, was, along with many others in his immediate family, interested in psi.213Shils & Blacker (1996).
Johannes Maria Verweyen (1883–1945), philosopher, anti-Nazi resistance fighter, poet, wrote on parapsychology and occultism.214Vermeyen (1928).
Gerda Walther (1897–1977), philosopher, pioneer phenomenologist, also made important contributions to parapsychology and the study of schizophrenia.215Waithe (1995).
Aloys Wenzl (1887–1967), philosopher, dean and president at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, was an official observer at a 1954 conference on psi.216Anonymous (1957).
Writers, Artists
Jelly d’Arányi (1893–1966), violinist, participated in séances and channeled various messages. Sister of Adila Fachiri.217Duchen (2016).
LFrank Baum (1856–1919), writer, creator of the Oz series, attended spiritist séances and wrote about them.218Algeo (1986).
Ingmar Bergman (1918–2007), film and theatre director and author, recounted autobiographical ostensible psi phenomena.219Bergman (2005).
Algernon Blackwood (1869–1951), writer, declared that his interest in psychic matters was ‘in questions of extended or expanded consciousness’ and saw ‘the rapprochement between Modern Physics and so-called psychical and mystical phenomena’.220Blackwood (1938/1973), xiv, xviii.
Jorge Luis Borges (1899–1986), writer, published an appreciative foreword to a Spanish version of JW Dunne’s An Experiment with Time.221Borges (1988).
Victor Brauner (1903–1966), surrealist painter, considered himself also a visionary.222Cardeña, Iribas, & Reijman (2012).
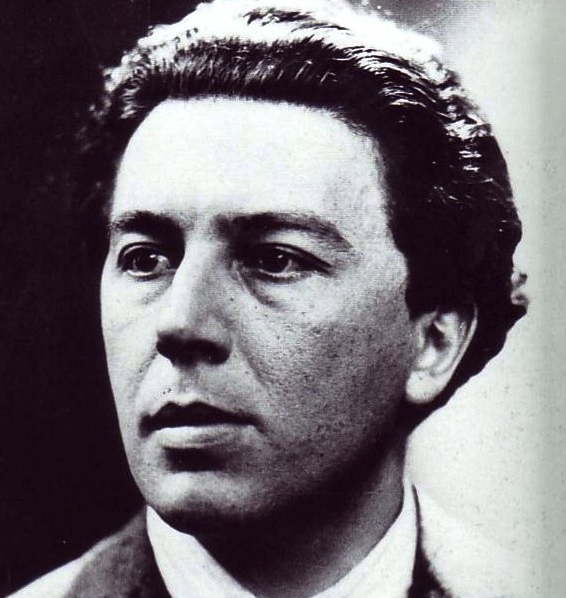
André Breton (1896–1966), founder of surrealism and knowledgeable of the psi literature, researched experientially and wrote extensively on psi and automatisms, often in collaboration with other surrealists.223Breton (1928/1964).
John W Campbell Jr (1910–1971), writer of science fiction (SF) and editor of Astounding Science Fiction during the golden age of science fiction. He discussed psi phenomena in his magazine and encouraged its inclusion into SF literature224Broderick (2018).
Gilbert Keith (GK) Chesterton (1874–1936), writer, best known perhaps for his Father Brown series, advocated an open investigation and consideration of psi phenomena.225Chesterton(1908).
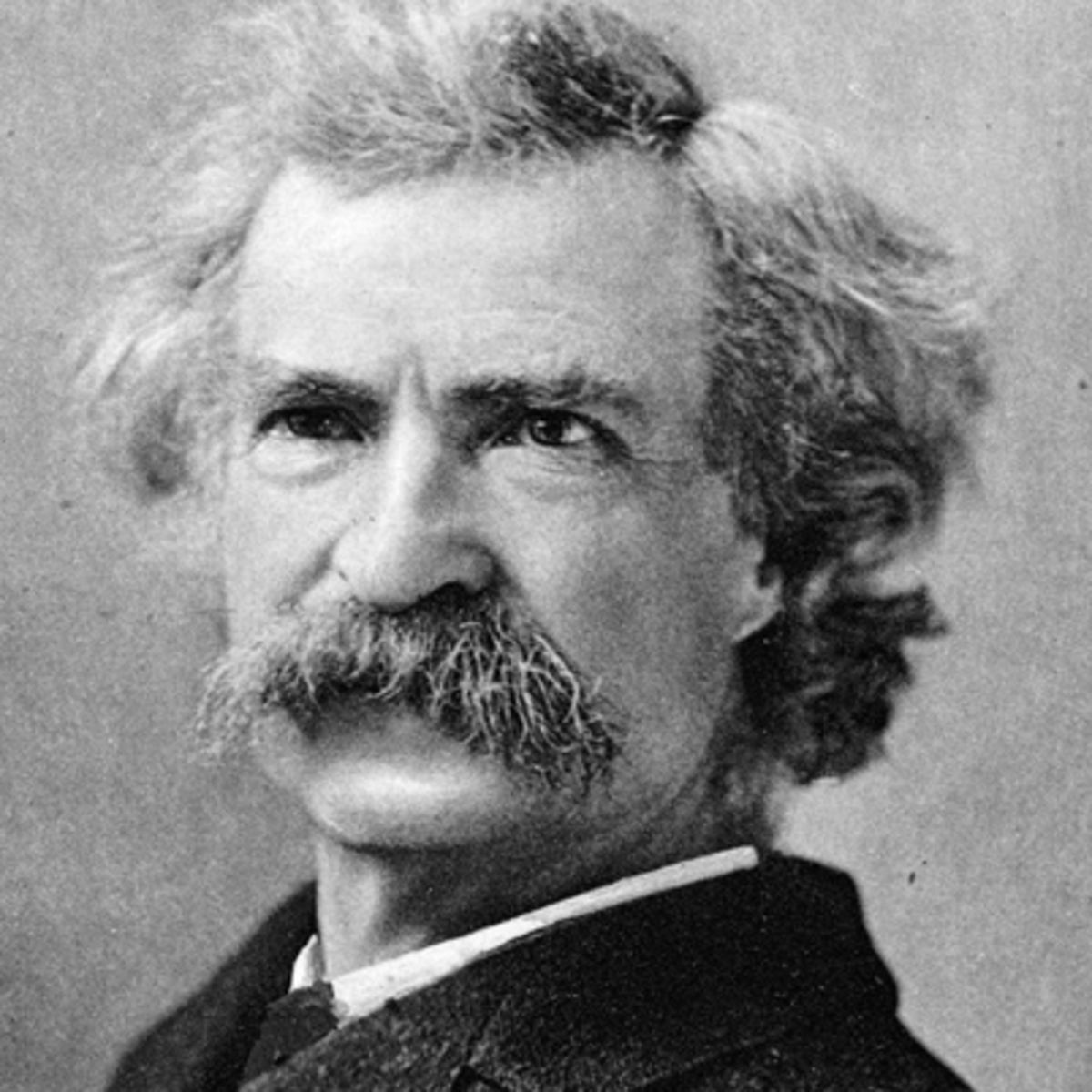
Samuel Clemens (Mark Twain) (1835–1910), writer, member of the American Society for Psychical Research, described various autobiographical psi events.226Ebon (1971).
Michael Crichton (1942–2008), writer, physician, and filmmaker, wrote about his personal experiences with psi.227Crichton (1988).
Rubén Darío (Félix Rubén García Sarmiento) (1867–1916), writer and diplomat pioneer of the modernismo literary movement. He referred to psychical researchers in his work (for instance, in his short story El caso de la señorita Amelia) and was interested in parapsychology, dreams, and spiritualism.228Anonymous (1997).
Robert Desnos (1900–1945), surrealist poet and automatist, claimed to have been in telepathic contact with another artist, Marcel Duchamp, and to see into other people’s future.229Conley (2008).
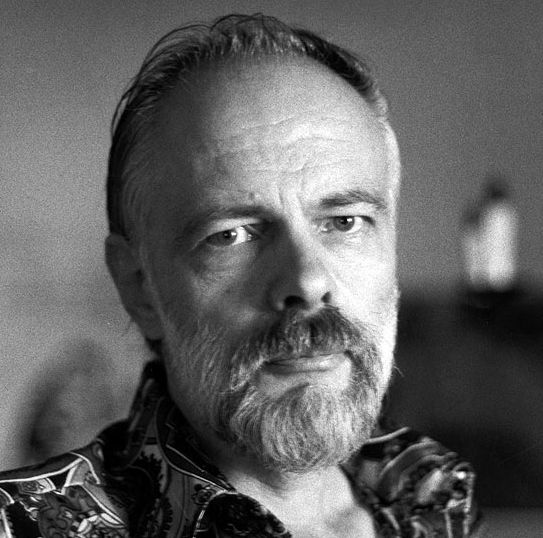
Philip K Dick (1928–1982), writer, described various ostensible psi phenomena in his autobiographical works, including xenoglossy and an accurate diagnosis of his son’s hernia.230Carrère (1993/2004).
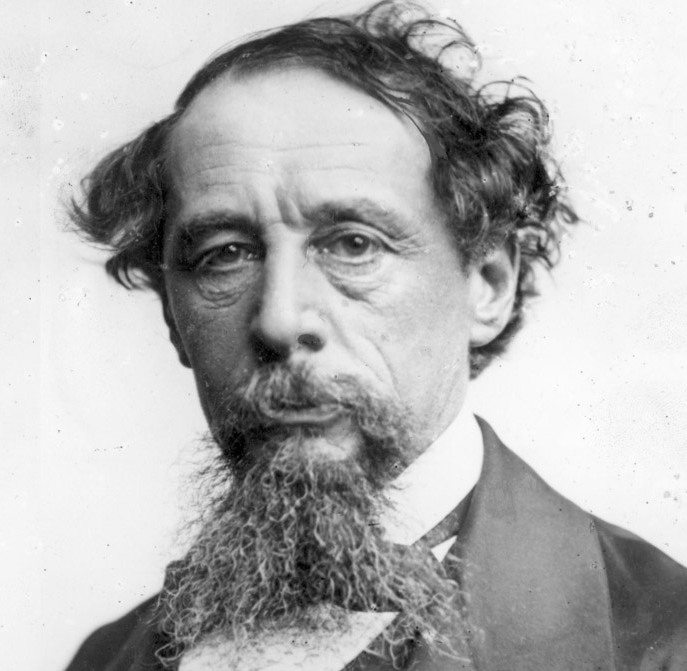
Charles Dickens (1812–1870), writer, member of The Ghost Club, organization devoted to psychical research.231http://www.ghostclub.org.
Charles Dodgson (Lewis Carroll) (1832–1898), author of Alice in Wonderland, mathematician, member of the Society for Psychical Research.232Blum (2006).
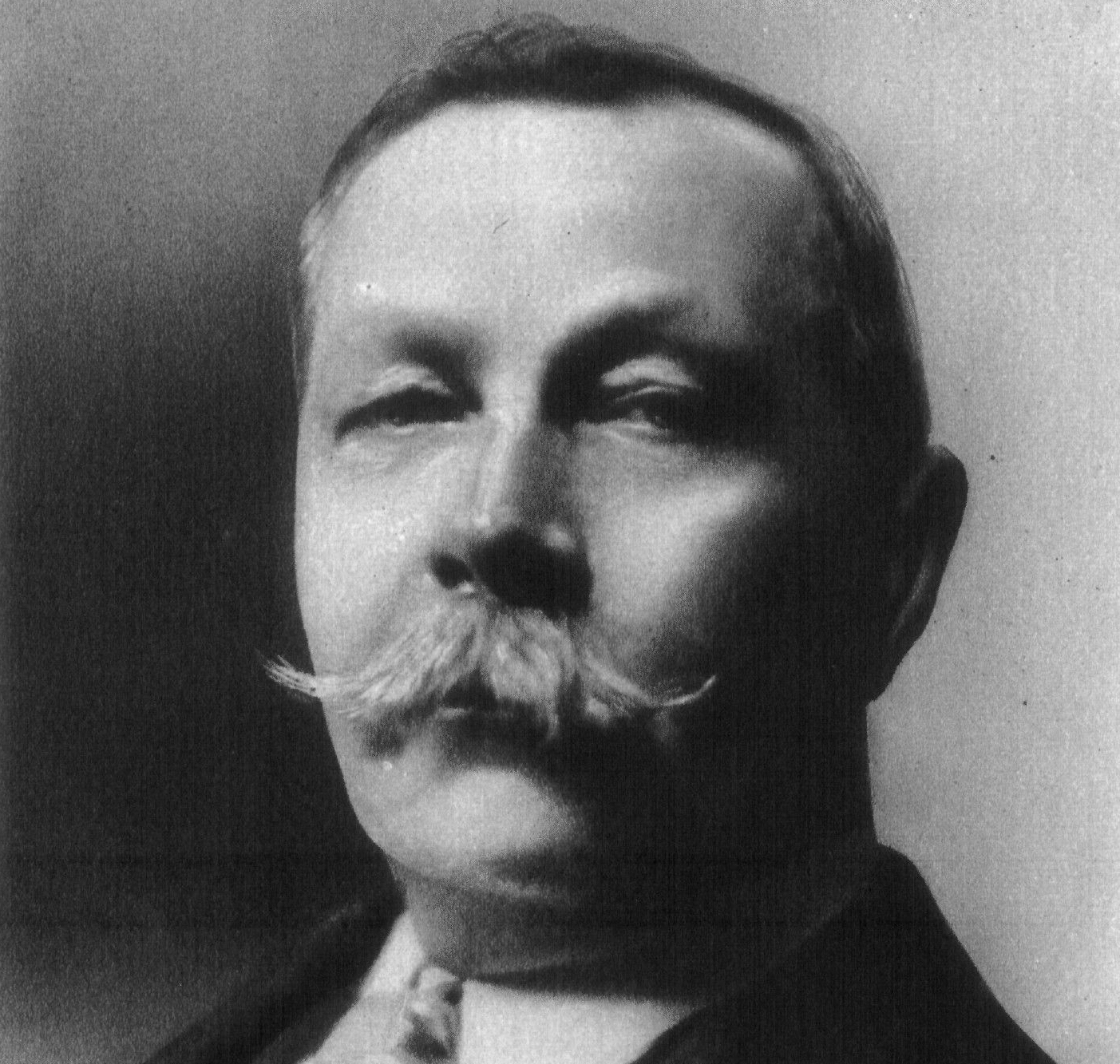
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle (1859–1930), creator of Sherlock Homes, unflinching defender of ostensible psi phenomena and spiritualism.233Doyle (1926). (See article)
Theodor Dreiser (1871–1945), writer and journalist, corresponded with psi researcher Hereward Carrington.234See collection here.
George Eliot (Mary Ann Evans) (1819–1880), writer, corresponded with psychical researchers and premised her The Lifted Veil on psi. She wrote to George Combe in 1852, ‘But indications of clairvoyance witnessed by a competent observer are of thrilling interest and give me a restless desire to get more extensive and satisfactory evidence.’235Haight (1954-1955).
Adila Fachiri (1886–1962), violinist, participated in séances and chanelled various messages. Sister of Jelly d’Arányi.236Duchen (2016).
Anne Francis (1930–2011), actress, winner of a Golden Globe and nominated for an Emmy, described her interest in psychic phenomena in her autobiography.237Francis (1982).
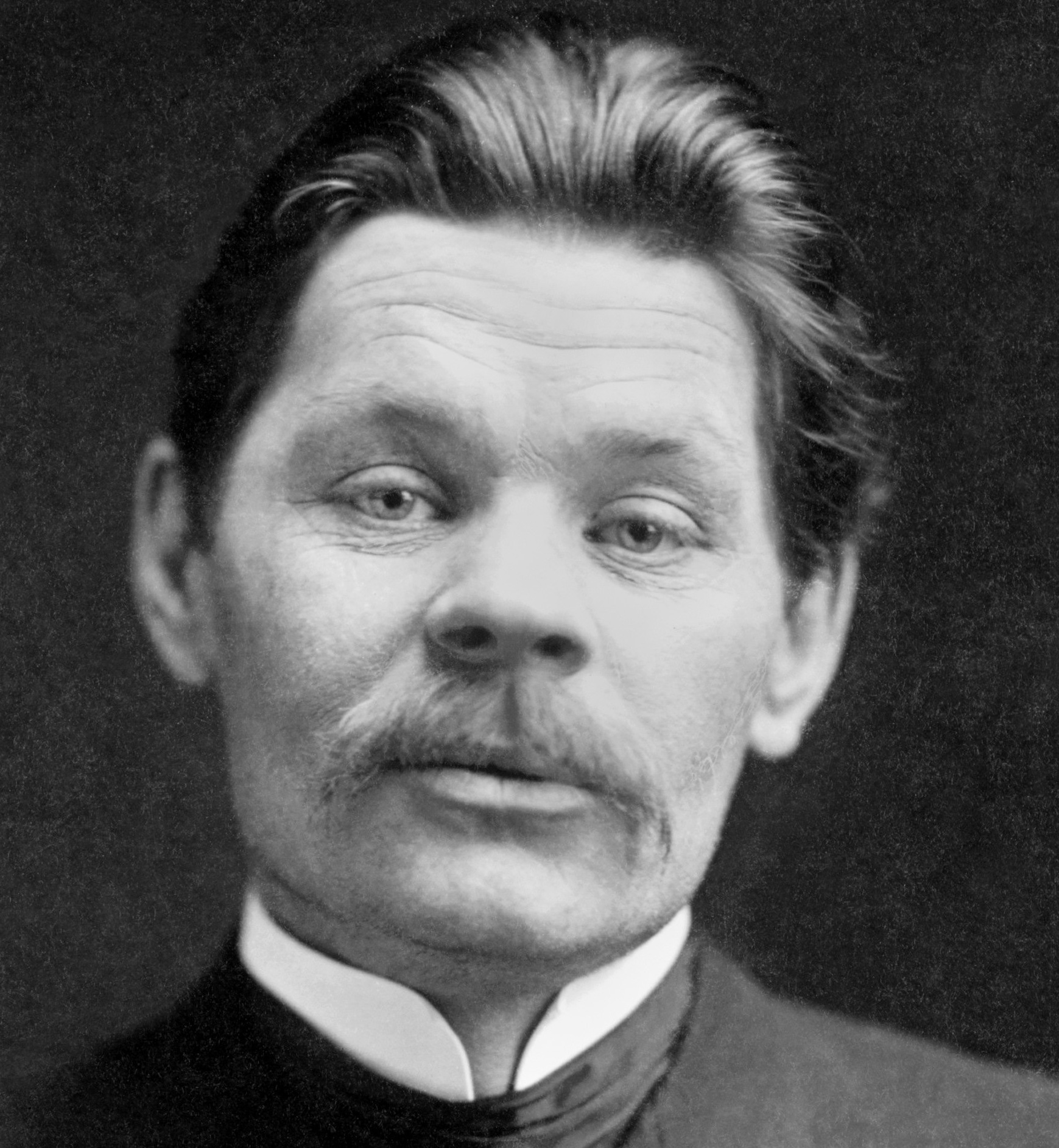
Maxim Gorky (1868–1936), writer, was convinced of the existence of telepathy.238Agursky (1977).
Graham Greene (1904–1991), novelist shortlisted for the Nobel Prize, was convinced that Dunne’s view of precognition was correct and explained some of his vision.239Stevenson (2018), 126.
Jerzy Grotowski (1933-1999), one of the most influential acting theoretician and theater/performance director in history. He was interested in psi phenomena and research.240Wolford (1998).
Alec Guinness (1914–2000), actor, wrote that he precognized the fatal accident of James Dean.241Guinness (1985).
Thomas Hardy (1840–1928), writer, claimed to have had one telepathic and other psi experiences.242Pinion (1968).
Victor Hugo (1802–1885), writer, creator of Les Misérables, experimented with automatic writing and drawing, participated in séances.243Dichter, Golinski, Krajewski, & Zander (2007).
Ted Hughes (1930–1998), British Poet Laureate, described psi phenomena in his life.244Hughes (1995).
Zora Neale Hurston (1891–1960), central figure of the Harlem Renaissance and important writer and anthropologist of Hoodoo and Vodou, had visions that she experienced as precognitions of her later life.245Kripal (2024).
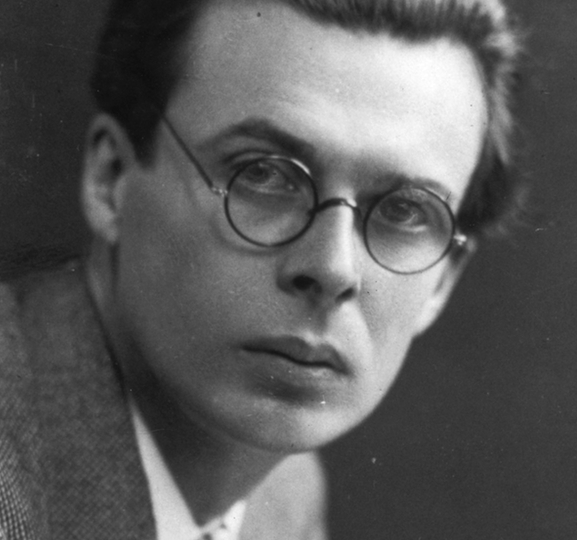
Aldous Huxley (1894–1963), writer, proponent of a Mind at Large, advisor to the Parapsychology Foundation.246Huxley (1954).
James Joyce (1882–1941), writer; his sister claimed that she and he had seen the ghost of their mother. He read and was influenced by Myers‘s Human Personality, and its Survival of Bodily Death.247Schneider (2015).
Wassily Kandinsky (1866–1944), painter and art theoretician, wrote about direct transmission of art.248Henderson (2002).
Hilma af Klint (1862–1944), painter, pioneer of abstractionism, worked as a medium with automatic writing, drawing, and painting.249Müller-Westermann & Widoff (2013).
Arthur Koestler (1905–1983), author, provided funds for what became the Koestler Parapsychology Unit of the University of Edinburgh, wrote on psi.250Koestler (1972). (See article)
Stanley Kubrick (1928–1999), film director, screenwriter, producer, etc., discussed psi positively as an inspiration for his film The Shining.251Ciment (n.d.).
Einar Hjörleifsson Kvaran (1859–1938), writer, editor, and spiritualist, participated in the investigations of Icelandic mediums including Indriði Indriðason and Hafsteinn Björnsson.252Swatos & Gissurarson (1997).
František Kupka (1871–1957), one of the founders of abstractionist art, proposed a direct mind-to-mind transmission of the artist’s inner world.253Henderson (2002).
Dame Edith Sophy Lyttelton (1865–1947), playwright, recipient of various awards including Dame Commander of the British Empire, wrote books about psi phenomena.254Willin (2021). (See article)
James Merrill (1926–1995), poet, winner of the Pulitzer Prize among other awards. Some of his work derives from sessions with a ouija board over the course of more than two decades.255Merrill (1982).
Robert Musil (1880–1942), writer, author of one of the foremost novels of the 20th century, The Man without Qualities, mentioned the possibility of psi phenomena during séances.256Hayasaka (2011), 168-69.
Vladimir Nabokov (1899–1977), writer, author of Lolita and other prose classics, kept a diary to test whether his dreams could anticipate future events, inspired by Dunne’s An Experiment with Time.257Andrews (2017).
Theodate Pope Riddle (1867–1946), pioneer and recognized early female architect, sat in and investigated the mediumship of Leonora Piper.258Gauld (2022).
JB Priestley (1894–1984), writer, supported the notion of precognition in his essays and plays.259Priestley (1989).
Marguerite Radclyffe-Hall (1880–1943), writer, pioneer of lesbian literature with The Well of Loneliness. She co-authored an important study of the medium Gladys Osborne Leonard.260Radclyffe-Hall & Troubridge (1919).
Rainer Maria Rilke (1875–1926), one of the foremost poet in German language, attended séances and experimented with automatic writing.261Barz (2010).
George Rochberg (1918–2005), composer, discussed psi phenomena in the context of his creative work.262Rochberg (1970).
Gene Rodenberry (1921–1991), writer and Star Trek creator, was convinced of the reality of psi phenomena.263Sutton (2006).
Jules Romains (Louis Henry Jean Farigoule) (1885–1972), writer, member of La Académie Française, wrote a book on sightless vision and alluded to psi in other writings.264Farigoule (1921).
John Ruskin (1819–1900), influential art critic, member of the Society for Psychical Research.265Blum (2006).
George William (AE) Russell (1867–1935), writer, painter, activist, claimed he was clairvoyant.266Boylan (1998).
Sigfried Sassoon (1886–1967), WWI poet, member of The Ghost Club.267See https://www.ghostclub.org.uk/
Victorien Sardou (1831–1908), writer, best-known for the libretto to Tosca, experimented with automatic writing and drawing.268Dichter et al. (2007).
Alvin Schwartz (1916–2011), fiction writer and essayist, discussed ostensible psi phenomena in his life.269Kripal (2011).
Upton Sinclair Jr (1878–1968), Pulitzer Prize winner, wrote a detailed account of psi experiments with his wife in his book Mental Radio.270Sinclair (2001). (See article)
Dame Edith Louisa Sitwell (1887–1964), poet and critic, helped direct some research with mediums.271Garrett (1968).
Olaf Stapledon (1886–1950), writer and philosopher, was interested in and recommended the scientific study of psi phenomena.272Crossley (1994).
William Thomas Stead (1849–1912), pioneer of investigative journalism and progressive activist who battled, among other topics, child prostitution. He published Borderland, a quarterly on psychic topics, described using automatic writing and telepathy, and repeatedly wrote about shipwrecks and himself as drowning after one, before perishing in the sinking of the Titanic. It was also claimed that he had communicated post-mortem. (See William T Stead.)273Shepard (1978), vol. 2, 879-80.
Rudolf Steiner (1861–1925), philosopher, theoretical founder of the Waldorf education system, wrote about personal psi experiences.274Steiner (2007).
Robert Louis Stevenson (1850–1894), author of Treasure Island, member of the Society for Psychical Research, corresponded with FWH Myers.275Stevenson (1994/1995).
Karlheinz Stockhausen (1928–2007), one of the most influential classical electronic and avant-garde musicians. He considered telepathy a fact in his statements.276See Stockhausen (1978).
August Strindberg (1849–1912), writer, painter and playwright, discussed personal experiences that he interpreted as parapsychological in his writings.277Strindberg (1896/1979).
Newton Booth Tarkington (1869-1946), twice won the Pulitzer Prize for fiction and wrote The Magnificent Ambersons, among other novels. He wrote the introduction to the suffragist May Wright Sewall’s book on her psychic experiences Neither Dead nor Sleeping. 278Sewell (1920).
Andrei Tarkovsky (1932–1986), film and theatre director and writer, discussed ostensible psi phenomena as sources for his films.279Garrett (1988).
Alfred, Lord Tennyson (1809–1892), Poet Laureate of Great Britain and Ireland, member of the Society for Psychical Research.280Blum (2006).
Jacques Tourneur (1904–1977), director of various acclaimed horror films, including Cat People. He was considered to be a psychic himself.281Wilson (1903).
Kurt Vonnegut Jr (1922–2007), author of Slaughterhouse Five, artist, described ostensible psi phenomena that occurred in his life.282Vaughan (1973).
Florizel von Reuter (1890–1985), violinist and composer, professor at the Vienna Musical Academy, wrote on his experience as a medium.283Reuter (1928).
H(erbert) G(eorge) Wells (1866–1946), writer of fiction and non-fiction, and futurist, President of PEN, author of The Time Machine and The War of the Worlds. His multi-volume summary of biology, co-authored with Julian Huxley and G.P. Wells, included a sympathetic and well-informed discussion of psychical research in Book 8, ‘Man’s Mind and Behaviour’ in Volume 3.284Wells, Huxley, & Wells (1929-1930).
Politicians, Explorers, Others
Alexander Aksakov (1832–1893), Russian State Councillor, writer, researched, contributed to and edited publications on psi.285Shepard (1978).
Arthur Balfour (1848–1930), philosopher, British prime minister, president of the Society for Psychical Research.286See here.
Gerald Balfour (1853–1945), scholar, Chief Secretary for Ireland, president of the Society for Psychical Research.287See here.
Donald Campbell CBE (1921–1967), speed record breaker in land and water, member of the Ghost Club.288See here.
Air Chief Marshal Hugh Dowding (1882–1970), commander of the RAF during the Battle of Britain, author of various books on survival and member of the Ghost Club.289See here.
Winifred Coombe Tennant (1874–1956), suffragette, politician, representative at the League of Nations, practised as a medium.290Oppenheim (1988).
Alexandra David-Néel (1868–1969), explorer, writer, expert on Tibet, declared that psychic phenomena should be studied ‘just like any other science’.291David-Néel (1971).
Robert “Bobby” Fischer (1943-2008), the eleventh World Chess Champion, wrote confirming that a putative chess game with the dead Grand Master Geza Maroczy indicated a very high level of chess playing.292Targ (2012).
Willliam Gladstone (1809–1898), served as British prime minister four different terms, member of the Society for Psychical Research, commented that psi research ‘is the most important work in the world’.293Tyrrell (1954).
Walter B LaBerge (1924–2004), aerospace engineer and Under Secretary of the US Army and Assistant Secretary of NATO, oversaw and supported the Stargate remote viewing program.294cia.gov (1979).
Claiborne de Borda Pell (1918–2009), six-term US Senator, head of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, supported psi research.295Utts (1991).
William Lyon Mackenzie King (1874–1950), longest-serving prime minister of Canada, spiritualist.296Ebon (1971).
Loren McIntyre (1917–2003), photojournalist, discoverer of the furthermost source of the Amazon River. He described communicating telepathically with the chief shaman of a Majoruna tribe.297Popescu (1991).
Francisco I Madero (1873–1913), provided the intellectual basis to the Mexican revolution and became the nation’s first democratically-elected president, practised automatic writing and mediumship.298Krauze (1997).
Erik Kule Palmstierna (1877–1959), Swedish politician and diplomat, wrote books based on channelled material.299Duchen (2016).
Theodore Roosevelt (1858–1919), 26th President of the United States, was a member of the American SPR.300American Society for Psychical Research (1885).
Charlie Rose (1939–2012), long term representative of North Carolina (USA), member of the House Intelligence Committee, supported the Stargate parapsychology project.301North-Best (2017).
Sir Henry Morton Stanley (1841–1904), explorer and journalist, wrote about psi phenomena in his autobiography.302Stanley (1909).
Cort van der Linden (1846–1935), progressive Prime Minister of The Netherlands, was a member of the (British) Society for Psychical Research.303Ruickbie (2019).
Henry A Wallace (1888–1965), progressive Vice President of the United States, as well as other important posts. He was a sponsor of the Round Table Foundation, which sponsored research on parapsychology.304Garrett (1968).
Etzel Cardeña
Literature
Algeo, J. (1986). Oz – a notable Theosophist: L. Frank Baum. American Theosophist 74, 270-73. [Online reprint preserved by Internet Archive.]
Agursky, M. (1977). An occult source of socialist realism: Gorky and theories of thought transference. In The Occult in Russian and Soviet Culture, ed. by B.G. Rosenthal, 247-72. Ithaca, New York, USA: Cornell University Press.
Alvarado, C.S., & Evrard, R. (2013). Nineteenth century psychical research in mainstream journals: The Revue Philosophique de la France et de l’Etranger. Journal of Scientific Exploration 27/4, 655-89.
American Society of Psychical Research (1885). Proceedings of the American Society for Psychical Research 1-4, 52-54.
Andrews, S. (2017). For three months in 1964, Vladimir Nabokov wrote down his dreams every morning, pursuing a theory that time flows backward. [Web page, November 29.]
Anon. (1957). Proceedings of Four Conferences of Parapsychological Studies. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Anon. (1990). ASPR Newsletter 16/2, 19-20.
Anon. (1997). Anthropos 170-71, 3-12.
Asprem, E. (2010). A nice arrangement of heterodoxies: William McDougall and the professionalization of psychical research. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences 46, 123-43.
Assagioli, R. (1958). Parapsychological Faculties and Psychological Disturbances. London: Medical Society for Study of Radiesthesia.
Atreya, B.L. (1952). An Introduction to Parapsychology: Collected Papers on Psychical Research. Banaras, India: Kumar.
Bakan, D., Merkur, D., & Weiss, D.S. (2009). Maimonides’ Cure of Souls: Medieval Precursor of Psychoanalysis. Albany, New York, USA: State University of New York Press.
Baltzer-Jaray, K. (2016). Reinach’s phenomenology of foreboding: Battlefield notes, 1916-1917. In Early Phenomenology: Metaphysics, Ethics, and the Philosophy of Religion, ed. by B. Harding & M.R. Kelly, 67-87. London: Bloomsbury.
Barnard, G.W. (2012). Living Consciousness: The Metaphysical Vision of Henri Bergson. Albany, New York, USA: State University of New York Press.
Barz, C. (2010). Scientific spirit, spirituality, and spirited writing: Spiritualism between science, religion and literature. Tijdschrift voor Skandinavistiek 31, 1.
Beauregard, O.C. de (1975). Quantum paradoxes and Aristotle’s twofold information concept. In Quantum Physics and Parapsychology, ed. by L. Oteri, 91-108. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Bekhterev, V. (1962). Telepathy with dogs. Journal of the American Society of Psychical Research 41, 351-53.
Berger, H. (1940). Psyche. Jena, Germany: Gustav Fischer.
Bergman, I. (2005). Ingmar Bergman: Samtal på Fårö (Ingmar Bergman: Conversation in Fårö). Sveriges Radio.
Bjørnson, B. (1909). Wise-Knut. New York: Brandu’s.
Blackwood, A. (1973). Introduction to 1938 edition. In Best Ghost Stories. New York: Dover. [Originally published 1938.]
Blum, D. (2006). Ghost Hunters: William James and the Search for Scientific Proof of Life after Death. New York: Penguin.
Bohm, D. (1986). A new theory of mind and matter. Journal of the American Society for Psychical Research 80, 113-35.
Boirac, E. (1917). Our Hidden Forces: An Experimental Study of the Psychic Sciences. New York: Frederick A. Stokes.
Booth, B., & Mehew, E. (eds.) (1994/1995). The Letters of Robert Louis Stevenson. New Haven, Connecticut, USA: Yale University Press.
Borges, J.L. (1988). J.W. Dunne: Un experimento con el tiempo [J.W. Dunne: An experiment with Time]. In Biblioteca Personal, xx. Madrid: Alianza.
Bottazzi, F. (2011). Mediumistic Phenomena Observed in a Series of Sessions with Eusapia Palladino. Princeton, New Jersey, USA: ICRL. [Originally published 1909.]
Bowditch, H.P., Pickering, E.C., Watson, W., Hall, E.H., Minot, C.S., Jackson, C.C., & Pierce, J.M. (1886). Report of the committee on thought transference. Proceedings of the American Society for Psychical Research 1, 106-12.
Bowles, N., & Hynds, F. (1979). Psi Search: New Investigation of Psychic Phenomena that Separates Fact from Fiction. New York: Joanna Cotler Books.
Boylan, H. (1998). A Dictionary of Irish Biography (3rd. ed.). Boulder, Colorado, USA: Roberts Rinehart.
Breton, A. (1964). Nadja. Paris: Gallimard/Folio. [Originally published 1928.]
Broderick, D. (2018). Psience Fiction: The Paranormal in Science Fiction Literature. Jefferson, North Carolina, USA: McFarland.
Brooks, R.B. (2012, April 16). John Hammond Jr.’s telepathic experiments at Hammond Castle. History of Massachusetts Blog.
Burke, K. (1970). No word is an island: Some thoughts on the “creativity” of verbal automatism. In Psi Factors in Creativity, ed. by A. Angoff & B. Shapin, 184-97. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Burlingham, D. (1953). Child analysis and the mother. Psychoanalytic Quarterly 4, 69-92.
Butler, N.M. (1886). The progress of psychical research. Popular Science Monthly 29.
Camp, B.H. (1937). Statement in notes section. Journal of Parapsychology 1, 305.
Cardeña, E. (2011). On wolverines and epistemological totalitarianism. (Guest editorial). Journal of Scientific Exploration 25, 539-51.
Cardeña, E. (2014). A call for an open, informed study of all aspects of consciousness. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience (27 January). [Web Page.]
Cardeña, E. (2024). In memoriam: Robert Rosenthal (1933-2024): Affable giant of psychology and champion of honest science. Journal of Anomalous Experience and Cognition 4/1, 13-15. doi: 10.31156/jaex.26221
Cardeña, E., Iribas, A., & Reijman, S. (2012). Art and psi. Journal of Parapsychology 76, 3-25.
Cardeña, E., Lynn, S.J., & Krippner, S. (eds.) (2014). Varieties of Anomalous Experience: Examining the Scientific Evidence (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Carnap. R. (1963). Intellectual autobiography. In The Philosophy of Rudolf Carnap, ed. by P. Schilpp, 1-84. La Salle, Illinois, USA: Open Court.
Carrel, A. (1939). The Voyage to Lourdes. New York: Harper & Row.
Carrère, E. (2004). I Am Alive and You Are Dead: A Journey through the Mind of Philip K. Dick. New York: Picador. [Originally published 1993.]
Carrington, H. (1907). The Physical Phenomena of Spiritualism. Boston, Massachusetts, USA: Herbert B. Turner.
Carter, J. (2016). A Full Life: Reflections at Ninety. New York, USA: Simon & Schuster.
Chari, C.T.K. (1975). Parapsychology, quantum logic, and information theory. In Quantum Physics and Parapsychology, ed. by L. Oteri, 91-108. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Chauvin, R. (1985). Parapsychology: When the Irrational Rejoins Science. Jefferson, North Carolina, USA: McFarland.
Chesterton, G.K. (1908). Orthodoxy. London: John Lane.
Child, I.L. (1985). Psychology and anomalous observations: The question of ESP in dreams. American Psychologist 40, 1219-30.
Cia.Gov. (1979). Released declassified army document.
Ciba Foundation (1965). Symposium on ESP. Boston: Little Brown & Co.
Ciment, M. (n.d.). Kubrick on The Shining: An interview with Michel Ciment. [Web page.]
Clarke, A.C. (2001). Foreword. In Childhood’s End. New York: Rosetta.
Collectif (1891). Avis important. Annales des sciences psychiques 1/2, 73.
Conley, K. (2008). Robert Desnos, Surrealism, and the Marvelous in Everyday Life. Lincoln, Nebraska, USA: University of Nebraska Press.
Courtier, J. (1908). Rapport sur les séances d’Eusapia Palladino à l’Institut Général Psychologique en 1905, 1906, 1907 et 1908 (Report on the séances with Eusapia Palladino at the Institut général psychologique in 1905, 1906, 1907, and 1908). Mayenne, France: Impr. de C. Colinnovembre.
Crichton, M. (1988). Travels. New York: Alfred A Knopf.
Crossley, R. (1994). Olaf Stapledon. Speaking for the Future. Syracuse, New York, USA: Syracuse University Press.
David-Néel, A. (1971). Magic and Mystery in Tibet. Mineola, New York, USA: Dover. [Originally published 1929.]
De Martino, E. (1942). Lineamenti di Etnometapsichica. (Outline of Ethnometapsychics) In Problemi di Metapsichica, 113-39. Rome: Società Italiana di Metapsichica.
De Morgan, S.E. (1863). From Matter to Spirit. The Result of Ten Years Experience in Spirit Manifestations. London: Longman, Green, Longman, Roberts, & Green.
Derrida, J. (1981). Telépathie [Telepathy]. Furor 2, 5-41.
Dessoir, M. (1889). Die parapsychologie (Parapsychology). Sphinx 7/42 (June), 341-42.
Devereux, G. (ed.) (1953). Psychoanalysis and the Occult. London: Condor.
Dichter, C., Golinski, H.G., Krajewski, M., & Zander. S. (2007). The Message: Kunst und Okkultismus. Art and Occultism. Köln, Germany: Walther König
Dodds, E.R. (1934). Why I do not believe in survival. Proceedings of the Society for Psychical Research 42/135, 147-78.
Downard K.M. (2021). Joseph John Thomson Investigates the Paranormal (Historical Perspective). European Journal of Mass Spectrometry 27, 151-57.
Doyle, A.C. (1926). The History of Spiritualism (2 vols.). New York: George H. Doran Co. & London: Cassell & Co.
Driesch, M. (1933). Psychical Research: The Science of the Super-Normal. New York: Arno.
Ducasse, C.J. (1961). A Critical Examination of the Belief in Life After Death. Springfield, Illinois, USA: Charles C. Thomas.
Duchen, J. (2016). Romantic spirit. BBC Music (December), 54-57.
Dunne, J.W. (1981). An Experiment with Time. London: Papermac.
Duplessis, Y. (2002). Surréalisme et paranormal. L’aspect experimental du surréalisme (Surrealism and the Paranormal. The Experimental Aspect of Surrealism). Agnières, France: JMG.
Dyson, F. (2007). Foreword. In Extraordinary Knowing. Science, Skepticism, and the Inexplicable Powers of the Human Mind, by E.L. Mayer. New York: Random House.
Dyson, F. (2014). One in a million. New York Review of Books, 25 March.
Ebon, M. (1971). They Knew the Unknown. New York: Signet.
Eccles, J.C. (1982). Mind and Brain: The Many Faceted Problems. New York: Paragon.
Ehrenwald, J. (1978). Einstein skeptical of psi? Postscript to a correspondence. Journal of Parapsychology 42, 137-42.
Eliade, M. (2006). Folklore as an instrument of knowledge. In Mircea Eliade: A Critical Reader, ed. by B. Rennie, 25-37. London: Equinox. [Originally published 1937.]
Ellenberger, H. (1970). The Discovery of the Unconscious. New York: Basic Books.
Evrard, R. (2011). Pierre Curie, a foot in parapsychology? Mindfield 3/3, 14-18.
Eysenck, H.J., & Sargent, C. (1993). Explaining the Unexplained: Mysteries of the Paranormal. London: Prion.
Excerpta (1963). Journal of the Society for Psychical Research 42, 161.
Farigoule, L. (1921). La vision extra-retinienne et le sens paroptique (Extra-Retinal Vision and the Paroptic Sense) (3rd ed.). Paris: Éditions de la NRF.
Fechner, G.T. (1904). The Little Book of Life after Death. Boston, Massachusetts, USA: Little, Brown, & Company. [Originally published 1836.]
Feinberg, G. (1975). Precognition – a memory of things future. In Quantum Physics and Parapsychology, ed. by L. Oteri, 54-73. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Ferenczi, S. (1955). Final Contributions to the Problems and Methods of Psycho-Analysis, ed. by M. Balint. London: Hogarth.
Fisher, R.A. (1930): The statistical method in psychical research. Proceedings of the Society for Psychical Research 39, 189-92.
Fisher, R.A. (1924). A method of scoring coincidences in tests with playing cards. Proceedings of the Society for Psychical Research 34, 181-85.
Flammarion, C. (1907). Mysterious Psychic Forces. Boston, Massachhusetts, USA: Small, Maynard and Company.
Flew, A. (1970). Towards a validation of psi phenomena. In Psi Favorable States of Consciousnes, ed. by R. Cavanna, 18-22. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Flournoy, T. (2007). From India to the Planet Mars: A Study of a Case of Somnambulism. New York: Cosimo. [Original work published 1911.]
Francis, A. (1982). Voices from Home: An Inner Journey. Berkeley, California, USA: Celestial Arts.
Fraser, J.T. (1966). The Voices of Time: A Cooperative Survey of Man’s Views of Time as Expressed by the Sciences and by the Humanities. New York: Braziller.
Freeman, S. (2012). Why be good? Review of On What Matters by D. Parfitt. New York Review of Books 59/7, 52-4.
Fuller, R.B. (n.d.). Everything I know: Section 7. [Video and transcript.]
Funk, I.K. (1907). The Psychic Riddle. New York: Funk & Wagnalls.
Gamow, G. (1966). Thirty Years that Shook Physics: The Story of Quantum Ttheory. New York: Dover.
Garçon, M. (1929). La magie noire de nos jours. Revue Metapsychique 4 (July-August), 259-69.
Garrett, E. (1968). Many Voices: The Autobiography of a Medium. New York: G.P. Putnam and Sons.
Garrett, L.A. (1988). Andrey Tarkovsky — Enigma and Mystery. [Web page, April, preserved on Internet Archive.]
Gauld, A. (1968). The Founders of Psychical Research. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
Gauld, A. (2022). The Heyday of Mental Mediumship 1880s-1930s: Investigators, Mediums and Communicators. Hove, UK: White Crow Books.
Gieser, S. (2005). The Innermost Kernel: Depth Psychology and Quantum Physics. Wolfgang Pauli’s Dialogue with C.G. Jung. Berlin: Springer.
Gillespie, W.H. (1953). Extrasensory elements in dream elements. In Psychoanalysis and the Occult, ed. by G. Devereux, 373-82. London: Condor.
Gissurarson, L.R., & Haraldsson, E. (1998). The Icelandic physical medium Indridi Indridason. Proceedings of the Society for Psychical Research 57, 52-148
Goff, H. (2005). Science and the seance. BBC News.
Good, I.J. (1961). Letter to the editor. Journal of Parapsychology 25, 58.
Greville, T.N.E. (1938). Exact probabilities for the matching hypothesis. Journal of Parapsychology 2, 55-59.
Gruber, K. (1925). Parapsychologische Erkenntnisse (Parapsychological Findings). Munich: Drei Masken.
Guinness, A. (1985). Blessings in Disguise. New York: Random House.
Haight, G.S. (ed.) (1954–1955). The George Eliot Letters (9 vols.). New Haven, Connecticut, USA: New Haven Publishers.
Hardy, A. (1971). Parapsychology in relation to religion. In A Century of Psychical Research: The Continuing Doubts and Affirmations, ed. by A. Angoff & B. Shapin, 101-10. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Hastings, A. (1991). With the Tongues of Men and Angels. A Study of Channeling. Fort Worth, Texas, USA: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Hayasaka, N. (2011). Robert Musil und dere Genius Loci. Germany: Willhelm Fink.
Henderson, L.D. (2002). Boccioni, Kupka, and the ether of space. In From Energy to Information: Representation in Science and Technology, Art, and Literature, ed. by B. Clarke & L.D. Henderson, 126-50. Stanford, California, USA: Stanford University Press
Hernández Peón, R. (1968). A unitary neurophysiological model of hypnosis, dreams, hallucinations, and ESP. In Psi and Altered States of Consciousness, ed. by R. Cavanna & M. Ullman, 178-93. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Hillman, J. (1970). On the psychology of parapsychology. In A Century of Psychical Research: The Continuing Doubts and Affirmations, ed. by A. Angoff & B. Shapin, 177-87. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Horn, S. (2009). Dr. Arthur Holly Compton. (24 July.) [Webpage.]
Horn, S. (2009). Unbelievable: Investigations into Ghosts, Poltergeists, Telepathy, and Other Unseen Phenomena, from the Duke Parapsychology Laboratory. New York: Ecco.
Hughes, T. (1995). Difficulties of a Bridegroom. New York: Picador USA.
Huxley, A. (1954). The Doors of Perception. New York: Harper & Brothers.
Huxley, J. (1965). Introduction. In The Phenomenon of Man, by P.T. de Chardin, 11-28. New York: Harper.
Hyslop, J.H. (1906). Enigmas of Psychical Research. Boston, Massachusetts, USA: Herbert B. Turner.
Institut Métapsychique International (n.d.). Les anciens membres de l’IMI: Nous reproduisons ici les hommages rendus à quelques uns des anciens membres du Comité Directeur de l’IMI, publiés dans la Revue Métapsychique (R.M.). [Web page on IMI website.]
Jaffé, A. (1967). C.G. Jung and parapsychology. In Science and ESP, ed. by J.R. Smythies, 263-80. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
James, W. (1958). The Varieties of Religious Experience: A Study in Human Nature. New York: New American Library. [Originally published 1902.]
James, W. (1960). The final Impressions of a psychical researcher. In William James on Psychical Research, ed. by G. Murphy & R.O. Ballou, 309-25. New York: Viking. [Originally published 1909.]
Jordan, P. (1951). Reflections on parapsychology, psychoanalysis, and atomic physics. Journal of Parapsychology 15, 278-81.
Josephson, B. (n.d.) Brian Josephson’s home page. [Web page.]
Kaiser, D. (2011). How the Hippies Saved Physics: Science, Counterculture, and the Quantum Revival. New York: Norton.
Kelly, E.F., Kelly, E.W., Crabtree, A., Gauld, A., Grosso, M., & Greyson, B. (2007). Irreducible Mind: Toward a Psychology for the 21st Century. Lanham, Maryland, USA: Rowman & Littlefield.
Kihlstrom, J.F., & McConkey, K. (1990). William James and hypnosis: A centennial reflexion. Psychological Science 1/3, 174-78.
Kleinman, P.G. (1970). Talking with Isaac Bashevis Singer. The Harvard Crimson.
Koestler, A. (1972). The Roots of Coincidence. New York: Random House.
Krauze, E. (1997). Biografía del poder: Caudillos de la Revolución Mexicana (1910–1940) (Biography of Power: Caudillos of the Mexican Revolution (1910–1940)). Barcelona, Spain: Tusquets.
Kripal, J.J. (2010). Authors of the Impossible: The Paranormal and the Sacred. Chicago, Illinois, USA: University of Chicago Press.
Kripal, J.J. (2011). Mutants and Mystics: Science Fiction, Superhero Comics, and the Paranormal. Chicago, Illinois, USA: University of Chicago Press.
Kripal, J.J. (2024). How to Think Impossibly. Chicago, Illinois, USA: University of Chicago Press.
Kübler-Ross, E. (1991). On Life after Death. Berkeley, California, USA: Celestial Arts.
Littlewood, J.E. (1968). Statistical analysis in card-guessing. Journal of the Society for Psychical Research 44, 321-26.
Lodge, O. (1916). Raymond, or Life and Death. New York: George H. Doran.
Lombroso, M. (1909). After Death – What? Boston: Small, Maynard.
Lorenzato, J. (1978). La lévitation est-elle prouvée? (Is levitation proven?). Revue Psi International 4.
Lyttelton, E. (2008/1931). Our Superconscious Mind. Whitefish, Montana, USA: Kessinger.
Maeterlinck, M. (1922). The Great Secret. New Hyde Park, New York, USA: University Books.
Mann, T. (2005). An Experience in the Occult. Whitefish, Montana, USA: Kessinger.
Marcel, G. (1956). The Influence of Psychic Phenomena on My Philosophy. London: Society for Psychical Research.
Margenau, H. (1970). Principles of evidence in science and their application to parapsychology. In Psi Favorable States of Consciousness, ed. by R. Cavanna, 11-17. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Marmin, N. (2001). Métapsychique et psychologie en France 1880-1940. (Parapsychology and Psychology in France 1880-1940). Revue d’Histoire des Sciences Humaines 1/4, 145-71.
Mayer, E.L. (2007). Extraordinary Knowing: Science, Skepticism, and the Inexplicable Powers of the Human Mind. New York: Bantam Dell.
Mead, M. (1977). Introduction. In Mind-Reach: Scientists Look at Psychic Abilities, ed. by R. Targ & H. Puthoff, xv-xxii. New York: Delacorte.
Meehl, P.E., & Scriven, M. (1956). Compatibility of science and ESP. Science 123/3184, 14-15.
Merrill, J. (1982). The Changing Light at Sandover. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Métapsychique au Gabon (Parapsychology in Gabon). (1982).Revue Métapsychique 16, 162-68.
Mills, E.L. (2009). The Fluid Envelope of our Planet: How the Study of Ocean Currents became a Science. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: University of Toronto Press.
Mitchell, E.D. (1971). An ESP test from Apollo 14. Journal of Parapsychology 35, 89-107.
Müller-Westermann, I., & Widoff, J. (2013). Hilma af Klint: A Pioneer of Abstraction. Ostfildern, Germany: Hatje Cantz.
Murphy, G. (1961). Challenge of Psychical Research. A Primer of Parapsychology. New York: Harper Colophon.
Nicholson, M. (1988). Toni Morrison interview. [YouTube video.]
Noakes, R. (2019). Physics and Psychics: The Occult and the Sciences in Modern Britain. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
North-Best, E. (2017). Senate worried CIA’s psychic program was part of mind contol pact.
Oesterreich, T.K. (1921). Grundbegriffe der Parapsychologie (Basic Concepts of Parapsychology). Pfullingen, Germany: J. Baum.
Oppenheim, J. (1988). The Other World: Spiritualism and Psychical Research in England, 1850–1914. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Owen, A. (2004). The Darkened Room: Women, Power, and Spiritualism in Late Victorian England. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Pert, C. (1996). Molecules of Emotion: Why You Feel the Way You Feel. New York: Scribner.
Pinion, F.B. (1968). A Hardy Companion: A Guide to the Works of Thomas Hardy and Their Background. London: Macmillan.
Pippard, A.B. (1982). Invited address. Presentation at the 25th Annual Convention of the Parapsychological Association/100th Convention of the Society for Psychical Research, Cambridge.
Pleasant, H. (1964). Biographical dictionary of parapsychology with directory and glossary 1946-1996. Garrett Publications.
Polanyi, M. (1958). Personal Knowledge. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Popescu, P. (1991). Amazon Beaming. Middlesex, UK: Penguin.
Price, H. (1939). Fifty Years of Psychical Research: A Critical Survey. London: Longmans, Green & Co.
Priestley, J.B. (1989). Man and Time. London: Crescent. [Originally published 1964.]
Prince, W.F. (1928). Noted Witnesses for Psychic Occurrences. Incidents and Biographical Data with Occasional Comments. Boston, Massachusetts, USA: Boston Society for Psychic Research.
Radclyffe-Hall, M., & Troubridge, U. (1919). On a series of sittings with Mrs. Osborne Leonard. Proceedings of the Society for Psychical Research 30, 339-554.
Radin, D. (2006). Entangled Minds. Extrasensory Perception in a Quantum Reality. New York: Paraview.
Radin, D. (2015). Obituary: Richard G. Shoup, July 30, 1943–July 18, 2015. Mindfield 7, 103-4.
Rawson, D.C. (1978). Mendeleev and the scientific claims of Spiritualism. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 122, 1-8.
Reichbart, R. (2019). The Paranormal Surrounds Us: Psychic Phenomena in Literature, Culture and Psychoanalysis. Jefferson, North Carolina, USA: McFarland.
Reuter, F. von (1928). Psychical Experiences of a Musician. London: Simpkin, Marshall and the Psychic Press.
Richet, C. (1923). Thirty Years of Psychical Research: Being a Treatise on Metaphysics. New York: Macmillan.
Rochberg, G. (1970). A raid on the infinite. In Psi Factors in Creativity, ed. by A. Angoff & B. Shapin, 64-69. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Roy, A.E. (1990). A Sense of Something Strange: Paranormal Studies. London: Dog & Bone.
Royce, J. (1889). Report of the Committee on Phantasms and Presentiments. Proceedings of the American Society for Psychical Research 1, 350-428.
Ruickbie, L. (2019). The SPR at war. Paranormal Review 88, 8-13.
Sala, J., Cardeña, E., Holgado, M.C., Añez, C., Pérez, P., Periñán, R., & Capafons, A. (2008). The contributions of Ramón y Cajal and other Spanish authors to hypnosis. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis 56, 361-72.
Schaefer, H. (1952). Telepathie und Hellsehen – im Lichte der Wissenschaft (Telepathy and Clairvoyance – in the Light of Science). Die Umschau in Wissenschaft und Technik 52, 611-14.
Schegloff, E.A. (2003). On ESP puns. In Studies in Language and Social Interaction in Honour of Robert Hopper, ed. by P. Glenn, C.D., LeBaron, & J. Mandelbaum (531-32). Routledge.
Schiller, F.C.S. (1914). Philosophy, science, and psychical research: A presidential address. Proceedings of the Society for Psychical Research 27, 191-220.
Schneider, E.H. (2015). “Welcomers”: James Joyce and Frederic W.H. Myers. Journal of Modern Literature 38, 59-70.
Schultz, S. (2017). Robert Jahn, pioneer of deep space propulsion and mind-machine interactions, dies at 87. [Web page on the Princeton University website, 30 November.]
Schwartz, S.A. (2001). The Alexandria Project. Bloomington, Indiana, USA: iUniverse.
Schweitzer, A. (1931). Aus Meinem Leben und Denken [Out of My Life and Thought]. Leipzig: Felix Meiner Verlag.
Sewall, M. W. (1920). Neither dead nor sleeping. Indianapolis: Bobb-Merrill.
Shepard, L.A. (1978). Encyclopedia of Occultism and Parapsychology. (2 vols.). New York: Avon.
Sinclair, U. (2001). Mental Radio. Charlottesville, Virginia, USA: Hampton Roads. [Originally published 1930.]
Solzhenitsyn, A. (1973). The Gulag Archipelago 1918–1956: An Experiment in Literary Investigation. New York: Harper & Row.
Sommer, A. (2013). The naturalisation of the ‘poltergeist’. [Unpublished manuscript.]
Sommer, A. (2014). Oliver Lodge, Psychical Research and German Physicists: Heinrich Hertz and Max Planck. [Weblog, 8 March.]
Sorokin, P.A. (1951). Introduction. In The Psychic Source Book, ed. by A.J. Smith. New York: Creative Age Press.
Stanley, H.M. (1909). The Autobiography of Henry M. Stanley. New York: Houghton Mifflin.
Steiner, R.S. (2007). Esoteric Lessons 1904–1909. Herndon, Virginia, USA: SteinerBooks.
Stevenson, I. (2006). Half a career with the paranormal. Journal of Scientific Exploration 20, 13-21.
Stevenson, R. (2018). Reading the Times: Temporality and History in Twentieth-Century Fiction. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
Stobart, M.A. (1923). Ancient Lights. London: Kegan Paul.
Stockhausen, K. (1978). Ylém für 19 spieler/sänger. In Text zur Musik 4. Cologne: Verlag M. DuMont Schauberg.
Strindberg, A. (1979). Inferno/From an Occult Diary. Middlesex, UK: Penguin. [Originally published 1896–1897.]
Sutton, D. (2006). From Deep Space to the Nine. Fortean Times (November), 28-33.
Swanton, J.R. (1953). A letter to anthopologists. Journal of Parapsychology 17, 144-52.
Swatos, W.H., & Gissurarson, L.R. (1997). Icelandic Spiritualism: Mediumship and Modernity in Iceland. New Brunswick, USA: Transaction Publishers.
Targ, R. (2012). The Reality of ESP: A Physisicst}s Proof of Psychic Abilities. Wheaton, IL: First Quest.
Teilhard de Chardin, P. (1965). The Phenomenon of Man. New York: Harper Torchbooks.
Truzzi, M. (1987). On pseudo-skepticism. Zetetic Scholar 12-13, 3-4.
Turing, A.M. (1950). I. Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind 59, 433-60.
Tyrrell, G.N.M. (1954). The Personality of Man: New Facts and Their Significance. Melbourne, London, Baltimore: Penguin.
Utts, J. (1991). Replication and meta-analysis in parapsychology. Statistical Science 6, 363-403.
Van Peursen, C.A. (1959). Parapsychologie en Wijsgerige Bezinning (Parapsychology and philosophical reflection). Tijdschrift voor Parapsychologie 31, 1-3.
Vasiliev, L.L. (2002). Experiments in Mental Suggestion. Charlottesville, Virginia, USA: Hampton Roads.
Vaughan, A. (1973). Patterns of Prophecy. Stroud, UK: Hawthorne.
Vermeyen, J.M. (1928). Die Probleme des Mediumismus (The Problems of Mediumship). Stuttgart, Germany: Enke.
Waithe, M.E. (1995). A History of Women Philosophers: Vol. IV: Contemporary Women Philosophers, 1900–Today. Dordrect, Germany: Kluwer.
Walker, E.H. (1979). The quantum theory of psi phenomena. Psychoenergetic Systems 3, 259-99.
Walter, W.G. (1970). The contingent negative variation and its significance for psi research. In Psi Favorable States of Consciousness, ed. by R. Cavanna, 170-88. New York: Parapsychology Foundation.
Wells, H.G., Huxley, J.S., & Wells, G.P. (3 vols.) (1929–1930). The Science of Life. London: Waverly Publishing Co.
Willin, M. (2021). Edith Lyttelton. Psi Encyclopedia. London: The Society for Psychical Research.
Wilson, M.H. (1903). Jacques Tourneur ou la magie de la suggestion. Paris: Centre Pompidou.
Wolford, L. (1998). Grotowski’s art as vehicle: The invention of an esoteric tradition. Performance Research, 3/3, 85-96.
Yeats, W.B. (2013). The Collected Works of W.B. Yeats. Volume XIII: A Vision: The Original 1925 Version. New York: Scribner. [Originally published 1937, revision of 1925 publication.]
Young, A.M. (1976). The Reflexive Universe. New York: Delacorte Press.
Zinchenko, V.P., Leont’ev, A.N., Lomov, B.F., & Luria, A.R (1974). Parapsychology: Fiction or fact? Soviet Psychology 12/3, 3-20.